| CPC G16H 10/20 (2018.01) [A61B 5/164 (2013.01); A61B 5/165 (2013.01); A61B 5/4803 (2013.01); G09B 19/00 (2013.01); G10L 25/66 (2013.01); G16H 50/20 (2018.01); G16H 50/30 (2018.01); A61B 5/4088 (2013.01); A61B 5/7275 (2013.01); G06F 16/24 (2019.01); G10L 15/18 (2013.01)] | 27 Claims |
|
1. A system for identifying whether a subject is at risk of having a mental or physiological condition, comprising:
one or more computer processors; and
a memory comprising machine-executable instructions;
wherein, upon execution, the instructions cause the one or more computer processors to:
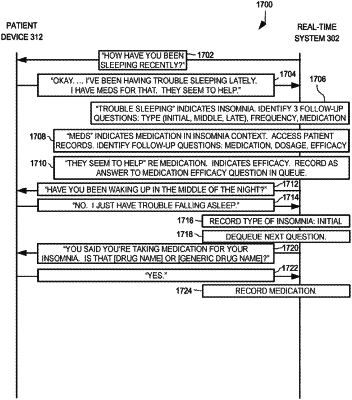
(a) obtain data from said subject, said data comprising speech data and optionally associated visual data;
(b) process said data using a plurality of machine learning models comprising a natural language processing (NLP) model and an acoustic model to generate an NLP output and an acoustic output, wherein said plurality of machine learning models comprises a neural network trained on labeled speech data collected from one or more other subjects, wherein said labeled speech data for each of said one or more other subjects is labeled as (i) having, to some level, said mental or physiological condition or (ii) not having said mental or physiological condition;
(c) fuse said NLP output and said acoustic output by (1) applying weights to said NLP output and said acoustic output to generate weighted outputs and (2) generating a composite output from said weighted outputs, wherein said NLP output and said acoustic output each comprise a plurality of outputs corresponding to a plurality of time segments of said speech data, and wherein said weights in (1) are temporally-based; and
(d) output an electronic report identifying whether said subject is at risk of having said mental or physiological condition, based at least on said composite output, which risk is quantified in a form of a score having a confidence level provided in said report.
|