| CPC G06T 7/593 (2017.01) [G06V 10/806 (2022.01); G06V 10/82 (2022.01); H04N 13/128 (2018.05); G06T 2207/10028 (2013.01); G06T 2207/20081 (2013.01); G06T 2207/20084 (2013.01)] | 15 Claims |
|
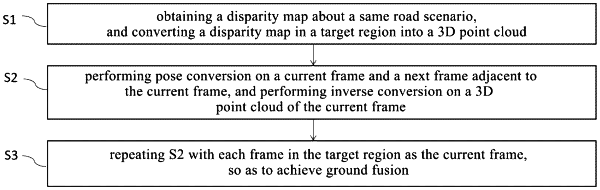
1. A real-time ground fusion method based on binocular stereo vision, comprising:
S1 of obtaining a disparity map for a same road scenario, and converting a disparity map in a target region into a three-dimensional (3D) point cloud;
S2 of performing pose conversion on a current frame and a next frame adjacent to the current frame, and performing inverse conversion on a 3D point cloud of the current frame; and
S3 of repeating S2 with each frame in the target region as the current frame, so as to achieve ground fusion,
wherein the disparity map in the target region is converted into the 3D point cloud according to
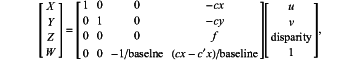 wherein u and y represent coordinates of a pixel in an image, disparity represents a disparity value of a corresponding pixel, f represents a focal length of a camera, cx and cy represent coordinates of an optical center of a left camera, c′x represents a coordinate of an optical center of a right camera, baseline represents a distance between the optical center of the left camera and the optical center of the right camera, and X, Y, Z and W represent homogeneous coordinates in a 3D coordinate system.
|