| CPC G06F 3/0635 (2013.01) [G06F 3/061 (2013.01); G06F 3/0658 (2013.01); G06F 3/0679 (2013.01)] | 11 Claims |
|
1. A data storage device, comprising:
a non-volatile memory comprising a plurality of memory dies; and
a controller configured to control the non-volatile memory and communicate with a host, wherein the controller is configured to:
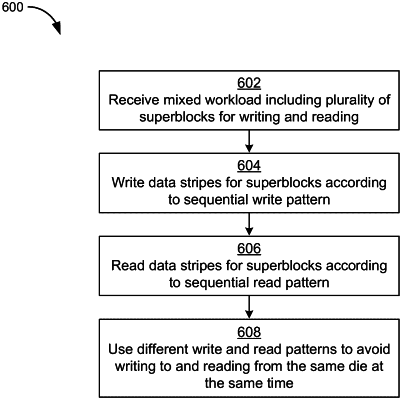
receive a mixed workload including a plurality of superblocks to be written to and read from the plurality of memory dies, each of the plurality of superblocks to be apportioned among the plurality of memory dies;
write a first data stripe associated with a first superblock of the plurality of superblocks to the plurality of memory dies according to a sequential write pattern; and
read the first data stripe associated with the first superblock from the plurality of memory dies according to a sequential read pattern, wherein:
the sequential write pattern causes the controller to write to the plurality of memory dies in a first order of memory dies; and
the sequential read pattern causes the controller to read from the plurality of memory dies in a second order of memory dies different from the first order of memory dies, and wherein:
the first order associated with the sequential write pattern is a random order, and the second order associated with the sequential read pattern is a sequential order; or
the controller is configured to, based on one or more future read operations, reorder the first order associated with the sequential write pattern to avoid writing to any memory dies of the plurality of memory dies while they are being read.
|