| CPC G02B 13/0045 (2013.01) [G02B 9/60 (2013.01)] | 15 Claims |
|
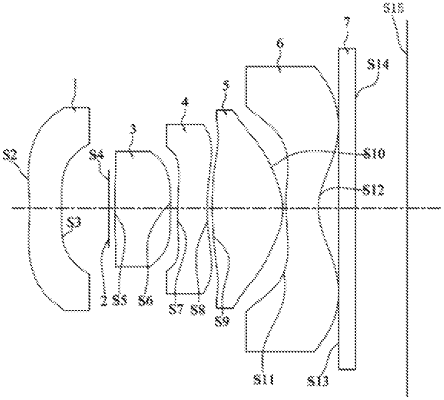
1. An imaging lens, wherein the imaging lens comprises five lenses, and from an object side to an imaging plane, the five lenses are as follows:
a first lens with a negative refractive power, wherein a paraxial region of an object side surface of the first lens is concave;
a second lens with a positive refractive power;
a third lens with a positive refractive power, wherein a paraxial region of an image side surface of the third lens is concave, and at least a portion away from an optical axis of the image side surface of the third lens is convex;
a fourth lens with a positive refractive power; and
a fifth lens with a negative refractive power;
wherein the imaging lens satisfies expressions:
3.163≤R6/R5<4;
0<f34/f<1;
6.682≤(V3−V5)<7;
0.797≤f2/f3<1; and
1.999≤|R4/R3|≤2.628;
where R5 represents a radius of curvature of an object side surface of the third lens, R6 represents a radius of curvature of the image side surface of the third lens, f34 represents a combined focal length of the third lens and the fourth lens, f represents a focal length of the imaging lens, V3 represents a dispersion coefficient of the third lens, V5 represents a dispersion coefficient of the fifth lens, f2 represents a focal length of the second lens, f3 represents a focal length of the third lens, R3 represents a radius of curvature of an object side surface of the second lens, and R4 represents a radius of curvature of an image side surface of the second lens.
|