| CPC B61L 27/20 (2022.01) [B60T 7/126 (2013.01); B61L 15/0062 (2024.01); B60T 2250/02 (2013.01); B60T 2250/04 (2013.01)] | 12 Claims |
|
1. A train braking control method supporting multi-stage deceleration, comprising following steps:
step 1, calculating an initial value Ek0 of kinetic energy of a train;
step 2, calculating work of traction force Wtraction of the train in a process from an initial position to traction removal;
step 3, calculating work of gravity force Wg of the train in a process from the initial position to a stop;
step 4, calculating work of braking force Wbraking of the train in a process from a braking application position to the stop;
step 5, calculating maximum allowable kinetic energy of the train among all restriction points from the initial position to a stop point;
step 6, obtaining kinetic energy Ek of the train according to following formula, determining whether the kinetic energy of the train exceeds the maximum allowable kinetic energy at the restriction point, if so, triggering emergency braking of the train, or else, operating the train normally:
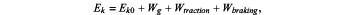 wherein a specific process of step 4 is as follows:
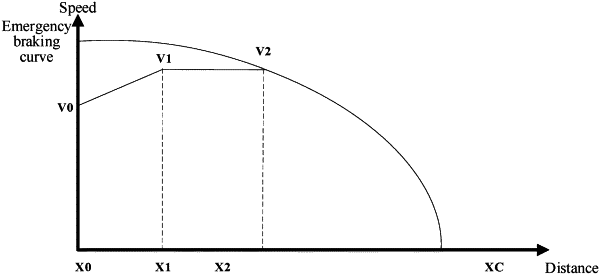
step A, calculating a velocity V reached by the train after a safe response time according to a current velocity of the train;
step B, calculating an emergency braking rate switching point;
step C, calculating work of braking Wbx of the train within a current deceleration interval;
step D, repeating step B to step C after entering a next deceleration interval, until the velocity is zero; and
step E, accumulating work of emergency braking force in all portions to act as total work of braking force Wbraking.
|