| CPC A63B 22/0605 (2013.01) [A61H 1/0214 (2013.01); A63B 21/00072 (2013.01); A63B 21/00076 (2013.01); A63B 21/00178 (2013.01); A63B 21/0058 (2013.01); A63B 21/0059 (2015.10); A63B 21/154 (2013.01); A63B 21/4034 (2015.10); A63B 22/0664 (2013.01); A63B 24/0062 (2013.01); A63B 24/0087 (2013.01); A63B 21/227 (2013.01); A63B 2022/0682 (2013.01); A63B 2024/0068 (2013.01); A63B 2024/0093 (2013.01); A63B 2071/009 (2013.01); A63B 2220/51 (2013.01); A63B 2220/62 (2013.01); A63B 2220/833 (2013.01); A63B 2225/50 (2013.01)] | 17 Claims |
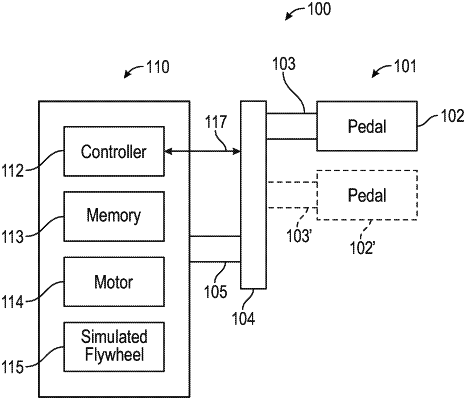
|
1. An exercise or rehabilitation electromechanical device comprising:
a drive sub-assembly comprising:
a first electric motor operably coupled to a controller;
a pedal assembly secured to the drive sub-assembly, the pedal assembly comprising:
a pedal configured to be engaged by a user,
a spindle mounted to the pedal and having a spindle axis,
a pedal arm assembly mounted to the spindle for support of the pedal arm assembly, and
a coupling assembly comprising a carriage that supports the spindle, and a second electric motor coupled to the carriage to linearly move the spindle, the coupling assembly being electrically actuated to selectively adjust a radial position of the pedal relative to a rotational axle in response to a control signal,
a housing with an elongate aperture through which the spindle extends, wherein the carriage is mounted in the housing to support the spindle, and the second electric motor linearly moves the spindle relative to the housing;
the pedal arm assembly is configured to be coupled to the rotational axle, the rotational axle is radially offset from the spindle to define a range of circumferential travel of the pedal around the rotational axle; and
at least one pressure sensor supported by the pedal to circumferentially rotate around the rotational axle with the pedal, and to sense a force applied to the pedal and transmit the force to the controller, the controller is configured to receive a pedal rotational position and, in response, send motor control signals to the first electric motor to cause the first electric motor to control rotational inertia at the pedal based on a pedal force value determined from the force applied to the pedal.
|