| CPC A61B 5/0205 (2013.01) [A61B 5/024 (2013.01); A61B 5/1118 (2013.01); A61B 5/4866 (2013.01); A61B 5/7278 (2013.01); A63B 24/0062 (2013.01); G16H 10/00 (2018.01); G16H 20/30 (2018.01); G16H 50/30 (2018.01); A63B 2024/0065 (2013.01); A63B 2220/30 (2013.01)] | 16 Claims |
|
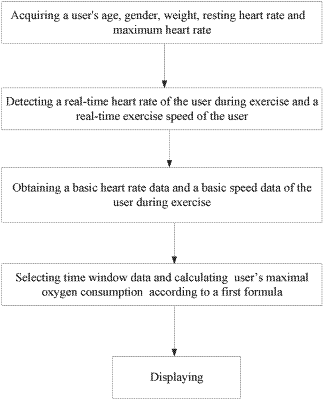
1. A computer-implemented method for dynamically acquiring maximal oxygen consumption (VO2max), comprising:
acquiring a user's age, gender, weight, resting heart rate and maximum heart rate;
detecting basic heart rate data through a heart rate sensor installed on a base carried by the user, the basic heart rate data comprising a plurality of exercise heart rates;
detecting basic speed data through a GPS system installed on the base, the basic speed data comprising a plurality of real-time exercise speeds, wherein the basic speed data is obtained by detecting the plurality of real-time exercise speeds through the GPS system and calculating based on the plurality of real-time exercise speeds through a method of condition screening;
calculating a characteristic average heart rate and a characteristic average speed based on the basic heart rate data and the basic speed data; and
calculating the user's maximal oxygen consumption according to the user's age, gender, weight, resting heart rate and maximum heart rate, the characteristic average heart rate and the characteristic average speed;
wherein the user's maximal oxygen consumption is calculated according to a first formula:
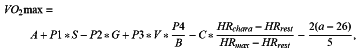 wherein A is a constant from 40 to 50, P1 is a constant from 7 to 8, S is a gender constant, male is equal to 1, and female is equal to 0; P2 is a constant from 0.1 to 0.2, G is user's weight; P3 is a constant from 4 to 5, V is characteristic average speed, P4 is a constant from 3 to 4, B is a constant from 1 to 2; C is a constant from 15 to 20, HRchara is characteristic average heart rate, HRrest is resting heart rate in a quiet state for user, HRmax is maximum heart rate; and a is user's age.
|