| CPC H04L 7/007 (2013.01) [H04L 27/0014 (2013.01); H04L 2027/0026 (2013.01)] | 6 Claims |
|
1. A frequency offset estimation method, applicable to a signal receiving end, wherein the signal receiving end is in communication with a signal sending end, and the method comprises steps of;
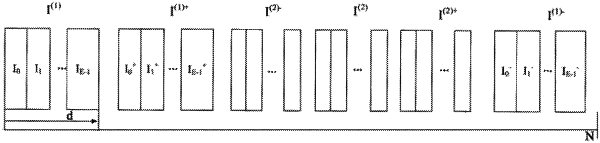
acquiring a main peak and a secondary peak of a PRACH signal when detecting that an access signal is in the PRACH signal sent by the signal sending end, wherein the PRACH signal is composed of a preset number of identical leader sequences;
calculating a ratio of a peak value of the main peak to a peak value of the secondary peak;
determining a first frequency offset according to the ratio and a preset subcarrier interval;
performing a frequency offset compensation on the PRACH signal according to the first frequency offset, to obtain a compensation sequence after the frequency offset compensation;
calculating a frequency offset between the compensation sequence and the leader sequences, to obtain a second frequency offset, so as to estimate a time delay of the access signal according to the second frequency offset;
acquiring a position of the main peak;
estimating a time delay of the access signal according to the position of the main peak and the second frequency offset, wherein according to a main peak point m′ and a number l of folds in integral folds of the frequency offset, a time delay position k is derived by calculation using a following formula, the access signal is expressed as:
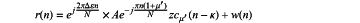 a correlation peak is expressed as:
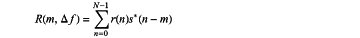 wherein if the number of folds of the frequency offset is not an integer, the peak point of the above formula m′=k, and the searched peak position m′ is a user time delay k; and if the number of folds of the frequency offset is an integer, the main peak point m′ and an actual time delay point k satisfy MOD(μ′l+κ,N)=m′,
wherein r(n) is the access signal, Δε is a frequency offset of the signal, Δε=Δf/fs, fs is a sampling rate, Δf is a frequency offset,
 w(n) is noise with a mean value of 0 and a variance of a σ2, μ is a root value, k represents an index value of a ZC sequence, N represents a length of a time domain sequence, n represents an index of the time domain sequence, and μ′ is dual to the root valueμ.
|