| CPC H04B 10/6971 (2013.01) [H04B 10/508 (2013.01); H04B 10/516 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
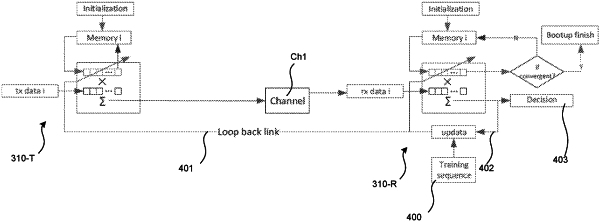
1. A method of communicating signals via a switching network for effecting point-to-point communication between nodes, the switching network having a time-varying switching configuration, which causes successive activation and deactivation of multiple channels of the switching network, a first channel of the channels connecting, when activated, a transmitter node and a first receiver node, and a second channel of the channels connecting, when activated, the transmitter node and a second receiver node, the method comprising:
in a training phase:
transmitting from the transmitter node via the first channel a first known training signal, to cause the first receiver node to receive a first distorted training signal,
using the first distorted training signal and knowledge of the first known training signal to determine one or more first transmit-side equalizer (EQ) coefficients, and
storing, in memory accessible to the transmitter node, the first transmit-side EQ coefficients, in association with the first channel,
transmitting from the transmitter node to the second receiver node a second known training signal, to cause the second receiver node to receive a second distorted training signal,
using the second distorted training signal and knowledge of the second known training signal to determine one or more second transmit-side EQ coefficients, and
storing, in memory accessible to the transmitter node, the second transmit-side EQ coefficients, in association with the second channel;
wherein, in a communication phase, the transmitter node uses an available schedule to determine, for each time interval of multiple time intervals, which of the first and second channels is activated, and uses the transmit-side EQ coefficients associated with that channel to pre-equalize signals prior to transmission in that time interval via that channel;
wherein at least one of the receiver nodes applies adaptive equalization to signals received from the transmitter node in the communication phase to account for time-varying channel conditions of the channel between that receiver node and the transmitter node.
|