| CPC H03H 9/02228 (2013.01) [H03H 9/02015 (2013.01); H03H 9/02559 (2013.01); H03H 9/02992 (2013.01); H03H 9/175 (2013.01); H03H 9/205 (2013.01); H03H 9/6406 (2013.01)] | 14 Claims |
|
1. An acoustic resonator device comprising:
a substrate having a surface;
a single-crystal piezoelectric plate attached to the surface of the substrate except for a portion of the piezoelectric plate forming a diaphragm that spans a cavity over the substrate in a thickness direction of the substrate that is orthogonal to the surface of the substrate;
an interdigital transducer (IDT) on a surface of the single-crystal piezoelectric plate such that interleaved fingers of the IDT are disposed on the diaphragm, the piezoelectric plate and the IDT configured such that a radio frequency signal applied to the IDT excites a primary shear acoustic mode in the diaphragm;
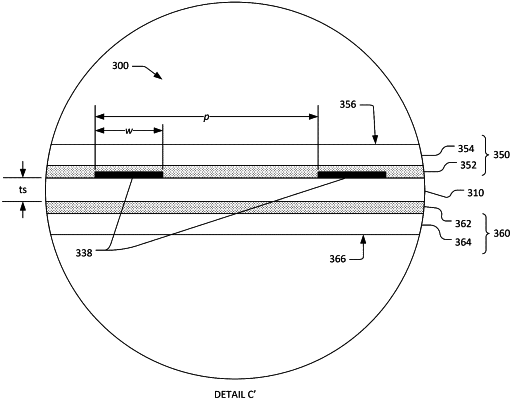
a back-side partial Bragg reflector on a back surface of the diaphragm, the back-side partial Bragg reflector consisting of a layer of low acoustic impedance dielectric material on the back surface of the diaphragm and a layer of high acoustic impedance dielectric material on the layer of low acoustic impedance dielectric material and opposite the diaphragm; and
a front-side partial Bragg reflector on a front surface of the diaphragm, with the front surface of the diaphragm opposing the back surface of the diaphragm, the front-side partial Bragg reflector consisting of a layer of low acoustic impedance dielectric material on the front surface of the diaphragm and a layer of high acoustic impedance dielectric material on the layer of low acoustic impedance dielectric material and opposite the diaphragm,
wherein each of the back-side partial Bragg reflector and the front-side partial Bragg reflector is structurally configured such that the respective reflectors do not reflect at least a portion of energy of an incident acoustic wave when the primary shear acoustic mode is excited in the diaphragm, and
wherein the primary shear acoustic mode is a bulk shear mode where acoustic energy propagates along a direction substantially orthogonal to the surface of the single-crystal piezoelectric plate and transverse to a direction of electric field created by the IDT.
|