|
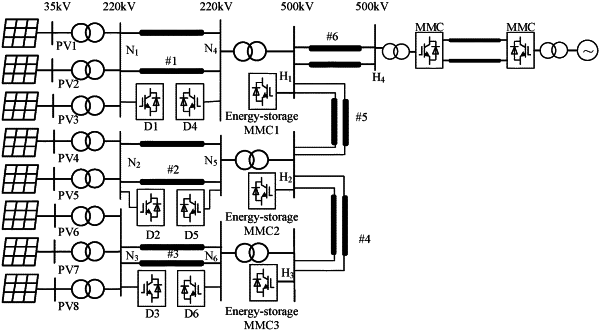
1. A backup voltage and frequency support method for a 100%-renewable energy sending-end grid, comprising: (Si) selecting a plurality of support nodes in the 100%-renewable energy sending-end grid; (S2) mounting a backup voltage and frequency support device at each of the plurality of support nodes; and (S3) dynamically adjusting an active power output of a renewable energy station of the 100%-renewable energy sending-end grid according to a frequency of a grid-connection point; wherein in step (Si), all nodes in the 100%-renewable energy sending-end grid are grouped according to voltage level; wherein voltage level includes 35 KV, 110 KV, 220 KV and 500 KV; wherein in step (S2),the backup voltage and frequency support device is an energy-storage modular multilevel converter (MMC); the energy-storage MMC comprises an energy storage device; the energy storage device is centralizedly arranged at a direct-current (DC) side of the energy-storage MMC or decentralizedly arranged in a sub-module of the energy-storage MMC through an interface circuit; and the energy storage device is formed by a plurality of energy storage elements connected in series or parallel, wherein the plurality of energy storage elements are batteries or supercapacitors; and the backup voltage and frequency support device adopts a power-synchronization control strategy; an active power control part of the power-synchronization control strategy is configured to calculate a difference between an active power instruction value and an active power actual value, and output a frequency compensation through a first-order lag element, wherein the active power instruction value is set to zero, and the difference is taken as an input of the first-order lag element; and a reactive power control part of the power-synchronization control strategy is configured to calculate a difference between an AC voltage setting value and an AC voltage actual value, and output a current instruction value through a proportional integral (PI) control, wherein the AC voltage setting value is set to 1.0 per unit (p.u.).
|