| CPC H02J 3/381 (2013.01) [H01L 31/0504 (2013.01); H02J 3/46 (2013.01); H02S 40/30 (2014.12); H02S 50/10 (2014.12); H02J 2300/26 (2020.01)] | 19 Claims |
|
1. A solar photovoltaic (PV) module for distributed solar electric power generation, the module comprising:
a plurality of strings of solar cells, each string comprising a plurality of solar cells electrically connected together, and further comprising a positive lead and a negative lead; and
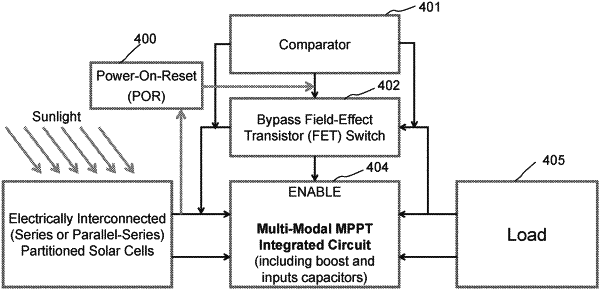
a plurality of multi-modal maximum-power-point tracking (MPPT) integrated circuits (ICs), each of said MPPT ICs having input terminals and output terminals, and having a pin structurally capable of enabling or disabling the MPPT IC function by the applied voltage on said pin being high or low, such that each string of solar cells is connected to the input terminals of a corresponding MPPT IC via the string's positive and negative leads;
wherein each of the plurality of MPPT ICs is enhanced with an add-on electronic circuit for protection of the corresponding MPPT IC and testing of the module;
wherein each add-on electronic circuit comprises a reverse-current-flow protection circuit coupled across the corresponding MPPT IC;
wherein each reverse-current-flow protection circuit comprises an active bypass circuit, enabling flash current-voltage testing and electro-luminescence testing of the module by bypassing and protecting the corresponding MPPT IC during reverse current flow opposite a photo-generated electrical current flow;
wherein each active bypass circuit comprises a bypass field effect transistor (FET) and a comparator, wherein said each comparator comprises electrical input leads that are connected to one of each of said input terminals and output terminals, and said comparator electrical input leads also connected to the source and drain of a corresponding bypass field-effect transistor (FET), with the combination of a comparator and a corresponding bypass field-effect transistor operating as reverse current flow detector and said reverse-current-flow protection circuit;
wherein each add-on electronic circuit further comprises a Power-On-Reset (POR) circuit operating to prevent and delay each of said MPPT ICs from turning on and operating as a power optimizer by disabling a corresponding MPPT IC via its pin voltage, and each Power-On-Reset (POR) circuit operating to turn on a corresponding bypass field-effect transistor (FET) during flash current-voltage testing.
|