| CPC G11C 11/1673 (2013.01) [G06F 7/5443 (2013.01); G06N 3/045 (2023.01); G06N 3/047 (2023.01); G11C 11/1675 (2013.01); G11C 11/1697 (2013.01); G11C 11/54 (2013.01)] | 26 Claims |
|
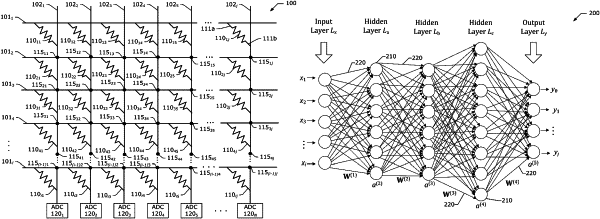
1. A probabilistic in-memory computing apparatus for a stochastic neural network (SNN), the apparatus comprising:
a plurality of input lines arranged parallel to one another;
a plurality of accumulation lines arranged parallel to one another and intersecting the plurality of input lines; and
a plurality of probabilistic bit devices (p-bits), wherein each p-bit of the plurality of p-bits is coupled to an input line of the plurality of input lines and an accumulation line of the plurality of accumulation lines, each p-bit is a time-varying resistance device that includes at least one bias terminal, the at least one bias terminal of each p-bit is capable of receiving a bias voltage, and the bias voltage is to cause a time-varying resistance of each p-bit to have a probabilistic resistance value based on a probability distribution of the SNN.
|