| CPC G06T 17/05 (2013.01) [G06F 18/29 (2023.01); G06T 7/74 (2017.01); G06V 20/20 (2022.01); G06V 20/58 (2022.01); G06T 2207/10016 (2013.01); G06T 2207/10028 (2013.01); G06T 2207/30244 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
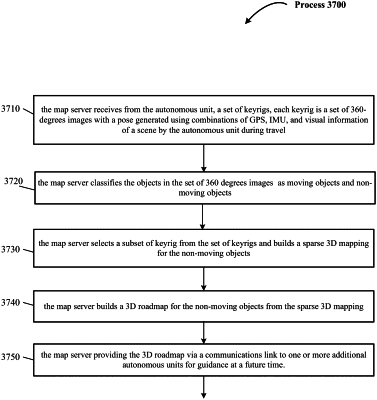
1. A method for building 3D maps from a surrounding scenery, including:
receiving from a first source, first visual information of the surrounding scenery and a position where the first visual information was captured;
classifying at least one of one or more objects from the first visual information of the surrounding scenery into a set of moving objects and a set of non-moving objects;
determining a sparse 3D mapping of object feature points taken from the first visual information of the surrounding scenery from the set of non-moving objects; and
building a first 3D map of object feature points from the sparse 3D mapping of object feature points.
|