| CPC G06F 11/079 (2013.01) [G06F 11/0736 (2013.01)] | 17 Claims |
|
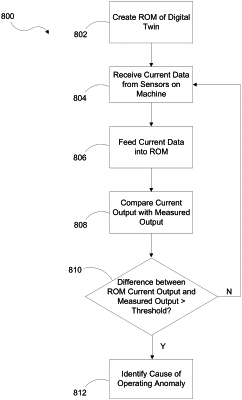
1. A method for identifying a cause of a machine operating anomaly, the method comprising:
creating a reduced order model (ROM) for a digital twin model of a selected machine type, including:
creating a plurality of reduced order models (ROMs) for the digital twin model for the selected machine type;
feeding historical data from a plurality of machines of the selected machine type into the plurality of reduced order models (ROMs) for the digital twin model and the digital twin model;
comparing an output from the digital twin model with an output from each of the plurality of reduced order models (ROMs) for the digital twin model; and
selecting, from the plurality of ROMs, a ROM with an output most closely matching the output of the digital twin model;
feeding current data from a deployed machine into the ROM;
comparing a current output from the ROM with a measured output from the current data;
determining that an operating anomaly exists when a difference between the current output and the measured output exceeds a selected anomaly threshold; and
identifying the cause of the operating anomaly, including:
feeding the current data into a plurality of fault models, wherein each fault model includes a particular component failure;
comparing a fault model output from each of the plurality of fault models with the measured output from the current data;
selecting a fault model with the fault model output most closely matching the measured output; and
displaying a component failure associated with the selected fault model as the cause of the operating anomaly.
|