| CPC G01H 9/004 (2013.01) [G01V 1/188 (2013.01); G01V 1/38 (2013.01)] | 5 Claims |
|
1. A swim bladder bionic amphibious optical fiber ocean acoustic sensor, comprising a plurality of overflow holes, a back cavity, a diaphragm supporting shell, a single-hole optical fiber sleeve, a coated optical fiber and a single-mode optical fiber, wherein a groove is arranged at a top of the diaphragm supporting shell, the groove is matched with the diaphragm outer frame, and the diaphragm outer frame is provided with a sound sensitive diaphragm; the top of the diaphragm supporting shell is provided with the overflow holes on an outer side of the groove, the back cavity is located in the diaphragm supporting shell, and the plurality of overflow holes are communicated with the back cavity; the single-hole optical fiber sleeve is installed at a bottom of the diaphragm supporting shell, a head of the coated optical fiber passes through the single-hole optical fiber sleeve and extends into the back cavity, and a tail end of the coated optical fiber is connected with the single-mode optical fiber;
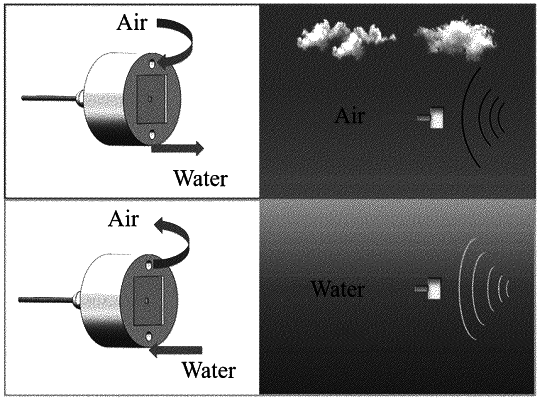
the overflow holes are capable of improving an ability of the sensor to resist hydrostatic pressure underwater, and a medium in the back cavity is capable of being replaced through the overflow holes, so as to realize conversion between different working states of the optical fiber ocean acoustic sensor and to achieve a purpose of amphibious use;
when the back cavity inside the sensor is inflated, the sensor acts as a fiber-optic microphone for acoustic detection and communication in air; when the back cavity inside the sensor is filled with water, the sensor acts as a fiber-optic hydrophone for underwater acoustic detection and communication;
the sound sensitive diaphragm is a square with a size of 0.5 mm×0.5 mm-1 mm×1 mm and a thickness of 200 nm-500 nm, and the diaphragm outer frame is a square with a size of 5 mm×5 mm and a thickness of 200 μm;
the diaphragm supporting shell has an overall diameter of 8 mm-12 mm, a height of 5 mm-10 mm, and the groove at the top has a size of 5.1 mm×5.1 mm×0.2 mm; and
a number of the overflow holes is 1-4, each of the overflow holes has a diameter of 0.2 mm-1 mm, a hole length of 0.5 mm-10 mm, and the back cavity has a volume of 20 mm3−400 mm3.
|