| CPC C07D 403/10 (2013.01) [A61P 35/04 (2018.01); C07D 237/04 (2013.01); C07D 401/10 (2013.01); C07D 405/10 (2013.01); C07D 413/10 (2013.01)] | 3 Claims |
|
1. A method of preparing a compound of general formula (I) having the structure:
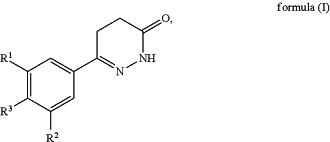 said method comprising the step of allowing an intermediate compound of general formula (II) to react:
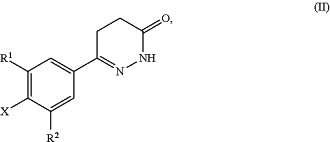 in which
R1 is selected from a hydrogen atom, a halogen atom, a cyano group, a C1-C3-alkyl group, a C1-C3-haloalkyl group, and a C1-C3-haloalkoxy group;
R2 is selected from a hydrogen atom and a halogen atom; and
X=F, Cl, Br, or I
to form the compound of general formula (I); wherein
a) if X=Cl, Br, or I, with the prerequisite that R1/R2 is not Cl, Br, or I, the method comprises allowing the compound of Formula (II) to react under transmetal catalyzed coupling conditions with a boronic acid of formula (IIIa)
(Rx)B(OH)2 (IIIa)
whereby Rx is
a C1-C6-alkoxy group,
a C2-C6-alkenyl group,
a C3-C6-cycloalkyl group,
a C5-C6-cycloalkenyl group,
a 3- to 7-membered heterocycloalkyl group, which is optionally substituted with one, two, or three substituents and each substituent is independently selected from a halogen atom, a C1-C3-alkyl group, a hydroxy group, NR4R5 group, a C1-C3-haloalkyl group and a C1-C3-haloalkoxy group,
a 5- to 7-membered heterocycloalkyl group which is partially unsaturated and optionally substituted with one, two or three substituents and each substituent is independently selected from an oxo group (═O), a C1-C3-alkyl group and a halogen atom,
an aryl group which is optionally substituted with one, two, three or four substituents and each substituent is independently selected from a halogen atom, a hydroxy group, a cyano group, a C1-C3-alkyl group, a C1-C3-haloalkyl group, a C1-C3-alkoxy group, a C1-C3-haloalkoxy group, a —C(O)NR4R5 group and a NR4R5 group;
a mono- or bicyclic heteroaryl group which is optionally substituted with one, two or three substituents and each substituent is independently selected from a halogen atom, a hydroxy group, a cyano group, a C1-C3-alkyl group, a C1-C3-haloalkyl group, a C1-C3-alkoxy group, and a NR4R5 group; or
a NR6R7 group,
R4/R5 is independently selected from a hydrogen atom, a C1-C6-alkyl group, a —C1-C5-alkylen-O—C1-C5-alkyl group, a —C1-C5-alkylen-S—C1-C5-alkyl group, C3-C6-cycloalkyl group, and a 3- to 5-membered heterocycloalkyl group;
R6/R7 is independently selected from a hydrogen atom, a C1-C6-alkyl group, a —C1-C5-alkylen-O—C1-C5-alkyl group, a —C1-C5-alkylen-S—C1-C5-alkyl group, a —C1-C5-alkylen-NR8—C1-C5-alkyl group, a —C1-C5-hydroxyalkylen-(C1-C3-haloalkyl) group, a C3-C6-cycloalkyl group, and a 3- to 5-membered heterocycloalkyl group,
or R6 and R7 together form a 3-, 4-, 5-, 6- or 7-membered ring optionally containing one or two additional heteroatoms selected from the group consisting of —O—, —S— and —NR8—,
and which is optionally substituted one, two, or three times with a substituent selected from a halogen atom, a hydroxy group, and a C1-C3-alkyl group
and if R6 and R7 together form a 5-, 6- or 7-membered ring, said ring can optionally contain a bridging group selected from a bond, —O—, —NR8—, —CH2—, —CH2—CH2—, —O—CH2—, —NR8—CH2 —;
R8 is a hydrogen atom or a C1-C3-alkyl group; or
a boronic ester of formula (IIIb)
(Rx)B(ORY)2 (IIIb)
wherein Rx is as defined for the boronic acid above and
Ry is C1-C6-alkyl, or the two residues Ry together form a pinacol ester, /potassium carbonate/a palladium catalyst selected from the following list:
dichlorobis(triphenylphosphine)palladium, tetrakistriphenylphosphinepalladium(0), palladium(II) acetate/triscyclohexylphosphine, tris(dibenzylideneacetone)dipalladium, bis(diphenylphosphineferrocenyl)palladium(II) chloride, 1,3-bis(2,6-diisopropylphenyl)imidazol-2-ylidene(1,4-naphthoquinone)palladium dimer, allyl(chloro)(1,3-dimesityl-1,3-dihydro-2H-imidazol-2-ylidene)palladium, palladium(II) acetate/dicyclohexyl(2′,4′,6′-triisopropyl-biphenyl-2-yl)phosphine, [1,1-bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene]palladium(II) chloride monodichloromethane adduct, [1,1′-Bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene]dichloropalladium(II), chloro(2-dicyclohexylphosphino-2′,4′,6′-triisopropyl-1,1′-biphenyl)[2-(2′-amino-1,1′-biphenyl)]palladium(II), or (2-Dicyclohexylphosphino-2′,4′,6′-triisopropyl-1,1′-biphenyl)[2-(2′-amino-1,1′-biphenyl)]palladium(II), preference being given to chloro(2-dicyclohexylphosphino-2′, 4′, 6′-triisopropyl-1, 1′-biphenyl)[2-(2′-amino-1, 1′-biphenyl)]palladium(II) in order to obtain a compound of formula (I) wherein R3 is Rx
or
b) if X=F, with the prerequisite that R1 is selected from a hydrogen atom, a halogen atom, a cyano group, and a C1-C3-haloalkyl group, and R2 is selected from a hydrogen atom and a halogen atom,
the method comprises allowing the compound of Formula (II) to react with HNR7R8;
optionally in the presence of a base, and optionally in the presence of an inert solvent, and optionally heat, up to the boiling point of the present solvent;
in order to obtain a compound of formula (I) wherein R3 is NR7R8.
|