| CPC B60H 1/22 (2013.01) [B60H 1/3204 (2013.01)] | 4 Claims |
|
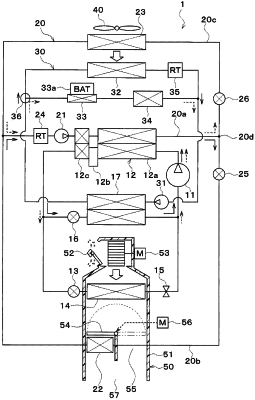
1. A refrigeration cycle device comprising:
a high-temperature heating medium circuit through which a high-temperature heating medium circulates;
an air heater configured to heat air blown into a cabin by exchanging heat between the high-temperature heating medium and the air;
a radiator configured to radiate heat to air outside the cabin by exchanging heat between the high-temperature heating medium and the air outside the cabin;
a compressor that sucks, compresses, and discharges a refrigerant;
a high-pressure-side heat exchanger configured to radiate heat from the refrigerant to the high-temperature heating medium by exchanging heat between the high-pressure refrigerant discharged from the compressor and the high-temperature heating medium;
a decompression part that decompresses the refrigerant subjected to the heat exchange by the high-pressure-side heat exchanger;
an evaporator that absorbs heat into the refrigerant decompressed by the decompression part to evaporate the refrigerant; and
a flow rate regulator that regulates a radiator-side flow ratio of a flow rate of the high-temperature heating medium flowing in the radiator to a flow rate of the high-temperature heating medium flowing in the high-pressure-side heat exchanger, wherein
a maximum outlet temperature that is a maximum value of a temperature of air heated by the air heater increases as the radiator-side flow ratio decreases, and
a rate of increase in the maximum outlet temperature with respect to a decrease in the radiator-side flow ratio increases as the radiator-side flow ratio decreases.
|