| CPC B29C 64/153 (2017.08) [B29C 64/264 (2017.08); B33Y 10/00 (2014.12); H05B 6/80 (2013.01); H05B 2206/046 (2013.01)] | 2 Claims |
|
2. A method of manufacturing a part from a powder, the method comprising:
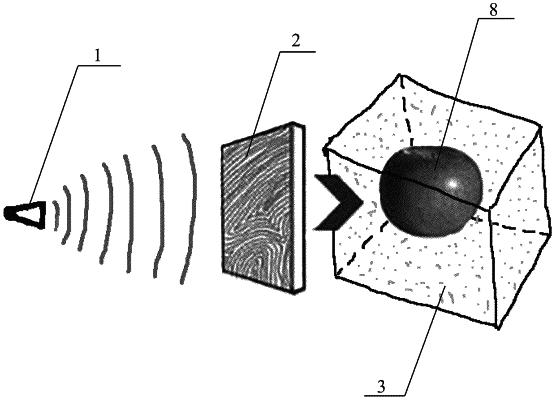
placing the powder with a particle size of maximum 1 mm in an air, gas, liquid or solid transit medium in an operating chamber;
creating a microwave field within the operating chamber with a microwave radiation power of 100 W to 150 MW and a frequency of 1 GHz to 10 THz, depending on physical properties of the powder, dimensions, degree of accuracy and complexity of geometric shapes of the part to be manufactured; and
developing, in the created microwave field, zones with an increased intensity of microwave radiation to develop heating zones of the powder corresponding to the zones with the increased intensity of microwave radiation, wherein the zones with the increased intensity of microwave radiation have shapes that follow a point, or a flat section or a spatial pattern of the part to be manufactured, wherein the increased intensity of microwave radiation results in a release of thermal energy sufficient to heat the powder to a sintering temperature of the powder in the heating zones, taking into account an initial temperature of the powder, and thereby sinter or melt the powder in the heating zones to produce the part;
wherein:
the thermal energy is generated by causing a microwave breakdown in determined areas being the heating zones, which occurs when an intensity of the microwave field in the heating zones exceeds a critical value due to at least one resonator focusing, on the determined areas, ionizing light or laser flux by a lens or a solid resonator, with the at least one resonator being moved in space over a respective layer of the powder to create the heating zones where the powder is sintered or melted in points corresponding to a geometric location of points of a determined two-dimensional layer of the part to be manufactured.
|