| CPC A61B 17/22 (2013.01) [A61M 25/0068 (2013.01); A61M 25/10 (2013.01); A61B 2017/00292 (2013.01); A61B 2017/22038 (2013.01); A61B 2017/22051 (2013.01); A61B 2017/22069 (2013.01); A61B 2017/22079 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
1. An endovascular method for gaining access to cervical arteries and treating intracranial and cervical vascular conditions, the endovascular method for placement a catheter system within a human vasculature between a groin and cerebral arteries comprising the steps of:
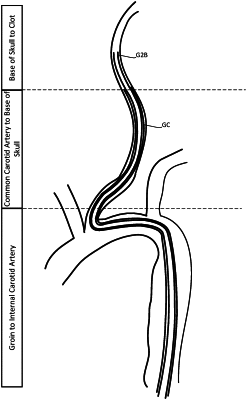
a. introducing a quadra-axial catheter system through a groin puncture, the quadra-axial catheter system comprising an outer guide catheter (GC) having a length sufficient to extend from the groin to an internal carotid artery, a groin to brain catheter (G2B) enabling aspiration through the G2B catheter and having a diameter to fit and slide within the outer GC, a luminal length longer than the outer GC and having a length sufficient to reach an intracranial clot, a soft distal tip region having a length sufficient to extend from the cervical internal carotid artery of a patient to cerebral arteries of a patient, and a proximal region having a length sufficient to extend from the carotid artery of a patient to outside the patient through the groin, a diagnostic catheter (DC) having a diameter to fit and slide within the G2B and having a pre-shaped tip for gaining access to varying anatomies of an aortic arch and having a length longer than the G2B, a guide wire (GW) having a diameter to fit and slide within the DC and having a length longer than the DC, where the soft distal tip region of the G2B has sufficient flexibility to ride over a DC without causing prolapse of the DC positioned beyond the aortic arch; and where the outer GC has a stiffness enabling the outer GC to ride over the G2B without causing prolapse of the G2B and DC when the G2B and DC are positioned beyond the aortic arch;
b. advancing the catheter system to a descending aorta;
c. advancing the GW and DC to a desired carotid artery and manipulating the GW into the desired carotid artery;
d. advancing the GW to the cervical arteries;
e. withdrawing the DC and introducing an alternate DC having a different tip region;
f. advancing the G2B over the GW and DC to the cervical arteries;
g. advancing the outer GC over the G2B to an internal carotid artery; and,
h. withdrawing the alternate DC and GW.
|