| CPC H04L 63/1416 (2013.01) [H04L 63/1441 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
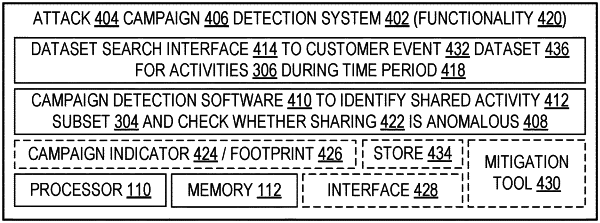
1. A computing system equipped for detecting a cybersecurity attack campaign against multiple customers of a service provider, the computing system comprising:
a digital memory;
a datasets search interface connectable to a first customer events dataset and to a second customer events dataset, the first customer events dataset representing activities that are ascribed to a first customer, the second customer events dataset representing activities that are ascribed to a second customer; and
a processor in operable communication with the digital memory, the processor configured to enhance cybersecurity by performing cybersecurity attack campaign detection steps which include (a) identifying via at least the datasets search interface a shared activity subset of the datasets which represents a shared activity, the shared activity being an activity that is ascribed to each of the customers, (b) determining whether customers' sharing of the shared activity is anomalous, (c) characterizing the shared activity as an indicator of a campaign attack when the sharing is anomalous, and (d) characterizing the shared activity as a non-indicator when the sharing is not anomalous;
wherein the computing system resides in an environment having M customer events datasets which represent activities ascribed to M respective customers, the shared activity is an activity that is ascribed to exactly N of the M customers, N is an integer greater than one, and M is an integer greater than or equal to N;
the processor is configured to calculate a statistical measure based on at least N and M, and the processor is also configured to determine whether sharing of the shared activity is anomalous based at least in part on the calculated statistical measure; and
wherein operation of the computing system reduces a security risk of overlooking an attack campaign whose footprint appears benign within any single customer's dataset.
|