| CPC H04J 3/0676 (2013.01) [H01Q 1/40 (2013.01); H01Q 17/00 (2013.01); H01Q 19/19 (2013.01); H04L 1/00 (2013.01); H04W 52/04 (2013.01); H04W 72/0453 (2013.01); H04W 72/12 (2013.01)] | 23 Claims |
|
1. A system comprising:
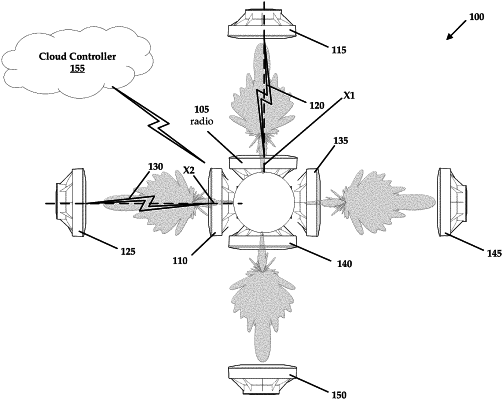
two or more radios collocated with one another, the two or more radios communicating with two far radios over a pair of long range wireless links, the two or more radios being configured to transmit and receive in synchronization with one another on a same channel, wherein an off-axis response for each of the two or more radios is reduced compared to their on-axis response for improved signal to noise ratio, the on-axis response for a radio occurring along a main axis between the two or more radios and the two far radios, and an off-axis response occurring when interference is experienced based on overlapping signals generated between any of the two or more radios and the two far radios, the on-axis response of each of the two or more radios being approximately equal to one another;
a cloud controller that monitors interference by determining any of the two or more radios that are not operating in synchronization with one another and selectively controls the two or more radios over a network; and
a spectral scanner that is configured to sense asynchronous broadcast periods.
|