| CPC G06Q 20/4016 (2013.01) [G06Q 20/425 (2013.01); H04L 63/0838 (2013.01); H04L 63/1416 (2013.01); H04L 63/1483 (2013.01)] | 12 Claims |
|
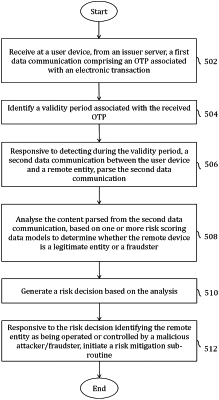
1. A method for securing electronic transaction one-time-passwords (OTPs) against phishing attacks, comprising implementing at a terminal device, the steps of:
generating, modifying, and refining one or more risk scoring data models based on one or more machine learning algorithms that identify correlations between financial terms, keywords, or other content within one or more previously received data communications, and whether a prior remote entity corresponding to the one or more previously received data communications has been identified as a malicious attacker;
receiving at the terminal device, a first data communication comprising an OTP associated with a requested electronic transaction;
identifying a validity period associated with the OTP;
receiving at the terminal device, during the identified validity period associated with the OTP, a second data communication from a remote entity;
detecting that the second data communication is received during the identified validity period associated with the OTP;
in response to detecting that the second data communication is received during the identified validity period associated with the OTP, extracting content from the second data communication;
analyzing the extracted content by using the one or more risk scoring data models that have been generated, modified, or refined by the one or more machine learning algorithms;
generating a risk decision based on output of the analysis of the extracted content, wherein the risk decision determines whether the remote entity comprises, or is controlled by, the malicious attacker; and
responsive to the risk decision determining that the remote entity comprises, or is controlled by, the malicious attacker, initiating a risk mitigation process.
|