| CPC G06N 3/065 (2023.01) [G06N 3/04 (2013.01); G06N 3/08 (2013.01)] | 21 Claims |
|
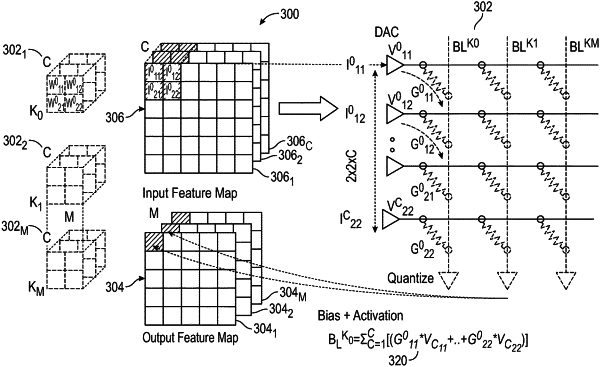
1. A method of performing multiply-accumulate operations in a neural network, comprising:
for individual networks of a plurality of networks arranged in one or more tiled columns, an individual network including a plurality of selectable parallel elements and each parallel element having a predetermined conductance value:
digitally reprogramming an equivalent conductance of the individual network, said digitally reprogramming including selecting one or more of the parallel elements of the individual network to map the equivalent conductance of the individual network to a single weight of a first partial selection of weights within the neural network, where the predetermined conductance values of the plurality of selectable parallel elements are not altered by said digitally reprogramming;
computing multiply-and-accumulate operations by mixed-signal computation using the one or more tiled columns by applying an analog voltage across each network to produce a first resultant current in each tiled column;
for individual networks of the plurality of networks:
digitally reprogramming the equivalent conductance of the individual network, said digitally reprogramming including selecting one or more of the parallel elements of the individual network to map the equivalent conductance of the individual network to a weight of a second partial selection of weights of the neural network, where the predetermined conductance values of the plurality of selectable parallel elements are not altered by said digitally reprogramming;
computing multiply-and-accumulate operations by mixed-signal computation using the one or more tiled columns by applying an analog voltage across each network to produce a second resultant current in each tiled column; and
repeating-the reprogramming and computing operations until computations for the neural network are completed.
|