| CPC G06N 10/00 (2019.01) [G06F 11/1004 (2013.01); G06F 30/20 (2020.01); G06N 10/20 (2022.01); G06N 10/40 (2022.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
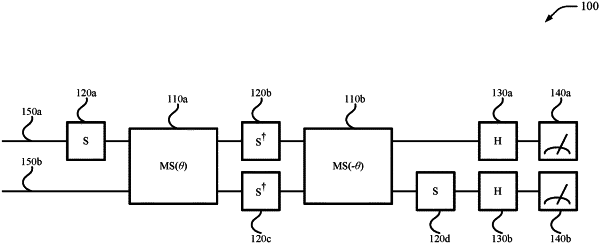
1. A method for handling asymmetric errors in quantum information processing (QIP) systems, the method comprising:
implementing a quantum circuit in the QIP system, the quantum circuit having at least a first qubit line and a second qubit line, wherein a first qubit state in the QIP system has a greater measurement error than a second qubit state in the QIP system;
swapping a first representation of the first qubit state and a second representation of the second qubit state at a quantum circuit level in response to at least one of the first qubit line and the second qubit line being expected to be at the first qubit state at a measurement; and
enabling a quantum simulation using the quantum circuit with the first qubit state and the second qubit state reassigned in at least one of the first qubit line and the second qubit line after the swapping of the respective representations.
|