| CPC G06F 1/3296 (2013.01) [G06F 1/324 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
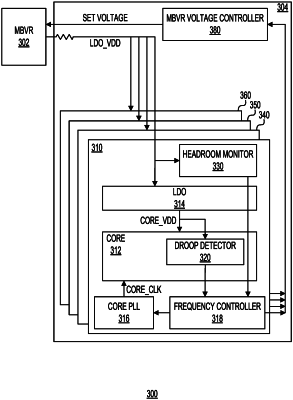
1. A system comprising: a system-on-chip (SoC) including a plurality of cores;
a voltage regulator module (VRM), based on a voltage set point associated with the VRM, configured to provide an input voltage to each of per core voltage regulators in the SoC, wherein each of the per core voltage regulators is configured to provide an output voltage to a corresponding core from among the plurality of cores; and
an adaptive voltage headroom control apparatus including: (1) a voltage controller for controlling the voltage set point associated with the VRM, (2) a per core voltage regulator headroom monitor, (3) a per core droop detector, and (4) a per core frequency controller configured to control a frequency of a core clock signal for a respective core from among the plurality of cores, wherein the adaptive voltage headroom control apparatus is configured to:
in response to either a detection of a headroom violation by the per core voltage regulator headroom monitor or a detection of a voltage droop by the per core droop detector, independently throttle operating frequency of a respective core clock signal, and
in response to either headroom violation events or droop events meeting a predetermined criterion: (1) lower the operating frequency of the respective core clock signal to a lowered operating frequency, (2) monitor headroom violation events and droop events at the lowered operating frequency, and (3) if the monitored headroom violation events or the monitored droop events at the lowered operating frequency continue to meet the predetermined criterion, change the voltage set point associated with the VRM to a second voltage set point corresponding to a higher voltage.
|