| CPC G06F 1/3296 (2013.01) [G06F 1/26 (2013.01); G06F 1/324 (2013.01); G06F 1/3206 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
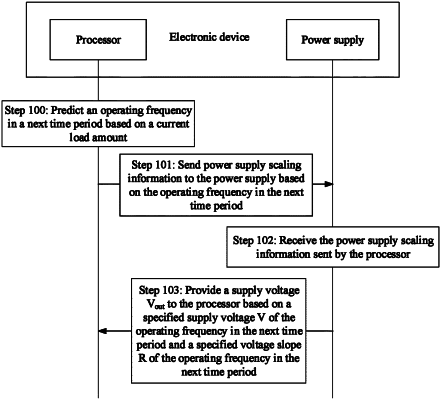
1. A voltage scaling method, comprising:
sending, by a processor of an electronic device, power supply scaling information to a power supply based on an operating frequency in a next time period, wherein the power supply scaling information comprises a specified supply voltage V of the operating frequency in the next time period which is defined as a specified supply voltage determined by the processor based on the operating frequency in the next time period, the operating frequency in the next time period is an operating frequency predicted based on a current operating frequency in a current time period, and the electronic device comprises the power supply; and
providing, by the power supply, a supply voltage Vout to the processor determined based on the specified supply voltage V of the operating frequency in the next time period and a specified voltage slope R of the operating frequency in the next time period, wherein
the voltage slope is a decrease speed indicative of an amount of change of the supply voltage Vout as a load current of the power supply increases; the supply voltage Vout decreases as the load current increases; and
Vmin≤Vout≤V, wherein Vmin is a lowest supply voltage for operation of the processor as the load current increases when the processor operates at the operating frequency in the next time period.
|