| CPC G01S 15/8904 (2013.01) [G01S 7/52085 (2013.01); G01S 15/8915 (2013.01); G01S 15/8959 (2013.01)] | 28 Claims |
|
1. An ultrasound imaging system comprising:
an ultrasound array comprising a plurality of ultrasound array elements;
control and processing circuitry operably connected to said plurality of ultrasound array elements, said control and processing circuitry comprising a processor and a memory, wherein said processor is configured to execute instructions stored in said memory for performing the steps of:
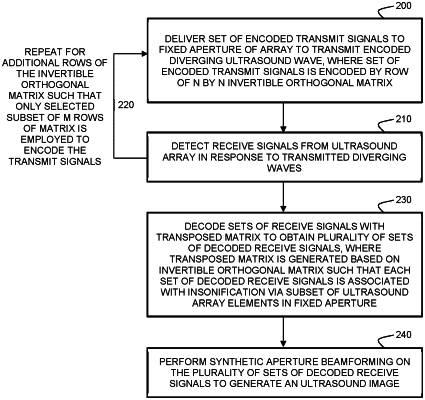
controlling the delivery of encoded transmit signals to the ultrasound array to sequentially transmit a plurality of diverging ultrasound waves, wherein each diverging ultrasound wave is generated by transmitting a respective set of encoded transmit signals to a fixed aperture of said ultrasound array, the fixed aperture consisting of N elements of the ultrasound array;
wherein each set of encoded transmit signals is encoded by a respective row of an N×N invertible orthogonal matrix such that only a selected subset of M rows of the invertible orthogonal matrix is employed to encode the transmit signals, wherein M<N;
said processor being further configured to process sets of receive signals received by the ultrasound array, wherein each set of receive signals is associated with transmission of a respective diverging wave, by:
decoding the sets of receive signals with a transposed matrix to obtain a plurality of sets of decoded receive signals, wherein the transposed matrix is generated based on the invertible orthogonal matrix such that each set of decoded receive signals is associated with insonification via a subset of the ultrasound array elements in the fixed aperture; and
performing synthetic aperture beamforming on the plurality of sets of decoded receive signals to generate an ultrasound image.
|