| CPC F25B 31/008 (2013.01) [F25B 41/31 (2021.01); F25B 43/02 (2013.01); F25B 49/02 (2013.01); F25B 2400/13 (2013.01); F25B 2600/2501 (2013.01); F25B 2600/2513 (2013.01); F25B 2700/191 (2013.01)] | 13 Claims |
|
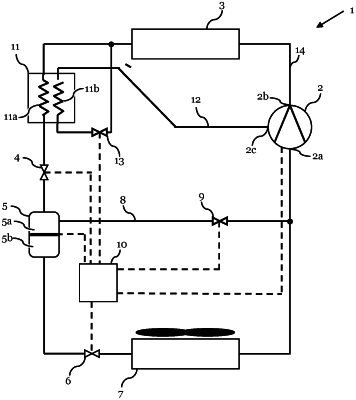
1. A method of controlling injection into a compressor in a refrigeration cycle, wherein the method is performed in a refrigeration cycle, which comprises at least an economizer heat exchanger, a heat rejection heat exchanger, a first expansion device, and a compressor configured for compressing the refrigerant, wherein the compressor comprises a means for compressing, a suction port, a discharge port, and an injection port, wherein the discharge port is connected to the heat rejection heat exchanger via a discharge line and wherein the injection port is connected to the means for compressing, and wherein the economizer heat exchanger comprises:
a first path, which has an input, which is connected to the heat rejection heat exchanger, and an output, which is connected to the first expansion device, and
a second path, which has an input, which is connected to the heat rejection heat exchanger via an economizer valve, and an output, which is connected to the injection port of the compressor via an injection line;
the method comprising:
regulating the economizer valve by using a first operation mode, which is based on a superheat level of the refrigerant in the economizer heat exchanger,
determining a pressure of the refrigerant in the injection line;
determining a temperature of the refrigerant in the discharge line; and
wherein the regulating comprises:
based on the determined pressure and the determined temperature, determining whether to proceed with regulating the economizer valve based on the superheat level of the refrigerant at the output of the economizer heat exchanger or whether to perform one of:
regulating the economizer valve by using a second operation mode based at least on the temperature of the refrigerant in the discharge line, or
regulating the economizer valve by using a third operation mode based at least on the pressure of the refrigerant in the injection line.
|