| CPC F02D 41/22 (2013.01) [F02D 41/30 (2013.01); F02M 51/00 (2013.01)] | 10 Claims |
|
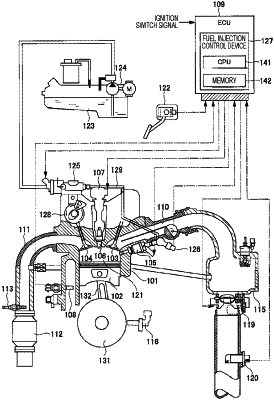
1. A fuel injection control device that controls a plurality of fuel injection valves each having a coil for energization, the fuel injection control device comprising:
a fuel injection pulse output unit that outputs an injection pulse signal for driving a fuel injection valve, based on a fuel injection instruction;
a drive state detection unit that detects a drive state of the fuel injection valve, from an energization current or an applied voltage of the coil of the fuel injection valve;
an injection abnormality detection unit that detects an injection abnormality of the fuel injection valve by comparing the fuel injection instruction with the drive state of the fuel injection valve; and
an injection abnormality detection execution determining unit that based on a state of an internal combustion engine, determines whether or not to permit execution of injection abnormality detection by the injection abnormality detection unit, and that when determining not permitting execution of the injection abnormality detection, prevents the injection abnormality detection unit from executing the injection abnormality detection, wherein
a state of the internal combustion engine refers to a drive state of the fuel injection valve, and indicates at least an interval between consecutively outputted injection pulse signals or a width of an injection pulse signal or a voltage applied to the coil or a rising timing of the injection pulse signal or a falling timing of the injection pulse signal, and
the injection abnormality detection execution determining unit does not permit execution of injection abnormality detection by the injection abnormality detection unit when at least either a crank angle at a target output timing of the injection pulse signal or a crank angle at a target stop timing of the injection pulse signal is equal to or larger than a given rotation angle from a control reference position of the internal combustion engine.
|