| CPC C07C 67/18 (2013.01) [C07C 245/12 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
1. A method for esterification of one or more carboxylic acid groups in a compound containing one or more carboxylic acid groups which comprises the step of reacting the one or more compounds with a diazo-compound of formula:
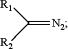 wherein the R1 and R2 groups of the diazo compound are selected such that the corresponding organic compound of formula:
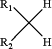 exhibits a —C—H pKa value between 18 and 29 as measured in DMSO;
wherein the one or more esters formed are bio-reversible;
wherein the reaction is carried out in buffered aqueous solvent at a pH between 5 and 7, in the absence of catalyst;
wherein the compound containing the one or more carboxylic acid groups is not an amino acid; and
wherein:
R1 comprises an electron withdrawing group selected from nitro, cyano, halogen, ammonium (—NR′3+), aryloxy, alkoxy, sulfonic ester (—SO2—R′), sulfonium (—S(R′)2+), phosphonium (—P(R′)3+), —COOR′, —COR′, —CON(R′)2, —OCOR′, alkylthio, arylthio, aryl, —C≡CR′, and —C═CR′2, where each R′ independently, is hydrogen, or an optionally substituted alky, alkenyl, alkynyl, aryl, alkylaryl, or arylalkyl, where two R′ on the same atom may together with that atom form a 5- to 8-member carbocyclic or heterocyclic ring in which one or more ring atoms can be replaced with —CO—, —O—, —CS—, —S— or —NR—, where R is hydrogen or an alkyl group having 1-3 carbon atoms; and
R2 is selected from the group consisting of an alkyl, aryl, alkyl aryl, heteroaryl, and heterocyclic group, each of which is optionally substituted.
|