| CPC B23K 26/34 (2013.01) [B23K 26/0624 (2015.10); B23K 2103/50 (2018.08)] | 23 Claims |
|
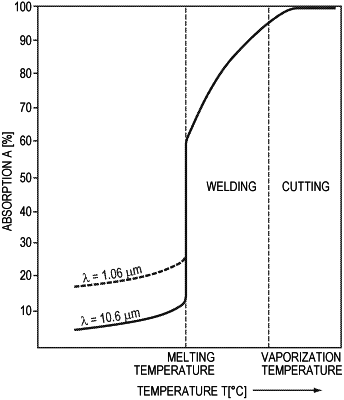
1. A method of processing a workpiece utilizing a laser system comprising a primary laser configured to emit a primary laser beam and a secondary laser configured to emit a secondary laser beam, wherein a wavelength of the primary laser beam is different from a wavelength of the secondary laser beam, the method comprising:
during a first stage, directing at least the secondary laser beam to a surface of the workpiece, whereby energy of the secondary laser beam is absorbed by the workpiece; and
during a second stage after at least a portion of the surface of the workpiece reacts to absorption of energy of the secondary laser beam, (i) directing the primary laser beam and the secondary beam to the surface of the workpiece, and (ii) thereduring, causing relative movement between at least the primary laser beam and the workpiece, whereby the workpiece is cut along a processing path determined at least in part by the relative movement,
wherein an output power of the secondary laser beam during the second stage is lower than an output power of the secondary laser beam during the first stage.
|