| CPC A61F 2/856 (2013.01) [A61B 17/3423 (2013.01); A61B 2017/00292 (2013.01); A61B 2017/3425 (2013.01); A61F 2250/0098 (2013.01)] | 15 Claims |
|
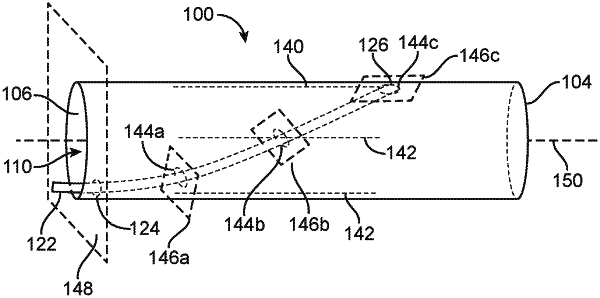
7. A neurovascular venous access system, comprising:
a tubular stent configured to be deployed in a venous sinus, the tubular stent having a sidewall defining a lumen, a proximal end opening, and an internal scaffolding disposed in the lumen and comprising one or more internal structural members; and
an elongate access catheter having a distal end portion configured to access the venous sinus,
wherein when the stent is deployed in the venous sinus, and the distal end portion of the catheter is inserted into the proximal end opening of the tubular stent, the one or more internal structural members of the tubular stent deflect the distal end portion of the catheter towards a wall of the venous sinus,
wherein the tubular stent defines a longitudinal axis, and wherein the one or more internal structural members of the tubular stent deflect the distal end portion of the catheter through an opening in the sidewall of the tubular stent, and
wherein the one or more internal structural members of the tubular stent deflect the distal end portion of the catheter through the sidewall opening of the tubular stent at an angle that is 20° to 45° relative to the longitudinal axis of the tubular stent.
|