| CPC A61B 6/4405 (2013.01) [A61B 6/4441 (2013.01); A61B 6/4447 (2013.01); A61B 6/547 (2013.01); A61B 6/032 (2013.01); A61B 6/035 (2013.01); A61B 6/4085 (2013.01); A61B 6/485 (2013.01); A61B 6/56 (2013.01)] | 17 Claims |
|
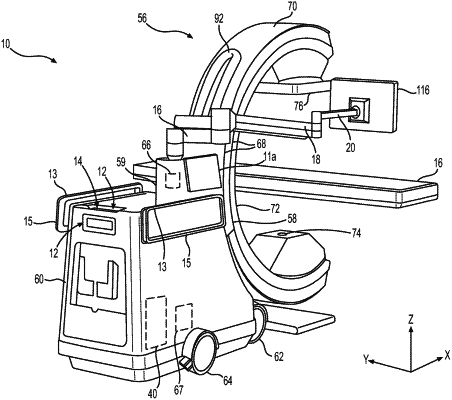
1. A method for imaging using a portable medical imaging system comprising a double telescoping C-gantry, an imaging signal transmitter and an imaging sensor, the method comprising:
positioning the imaging signal transmitter and the imaging sensor opposite to one another, wherein the imaging sensor defines an angle of incidence with respect to a signal emitted from the imaging signal transmitter, wherein the imaging sensor and imaging signal transmitter, in an initial position, define a central axis from the imaging sensor to imaging signal transmitter, the central axis being between the imaging sensor and the imaging signal transmitter and being the central axis of the gantry, and a first isocenter located at the central axis, the first isocenter being equidistant between the imaging signal transmitter and the imaging sensor,
wherein the angle of incidence is defined as a first line from a focal point of the imaging signal transmitter to a middle of the imaging sensor and a second line normal from the imaging sensor to the first isocenter, wherein the angle of incidence is zero at the initial position, and the imaging signal transmitter and the imaging sensor being attached to the double telescoping C-gantry;
controlling the movement of the telescoping C-gantry to minimize a zone of collision, the zone of collision being an annular area defined by an extent of possible positions for the imaging sensor,
recording a first signal from the positioned imaging signal transmitter using the positioned imaging sensor, so as to capture an image of a first portion of a field-of-view;
rotating the imaging sensor such that the angle of incidence changes while the second line remains normal from the imaging sensor to the first isocenter; and
recording a second signal from the imaging signal transmitter using the rotated imaging sensor, so as to capture an image of a second portion of the field-of-view.
|