| CPC A61B 5/7275 (2013.01) [A61B 5/0205 (2013.01); A61B 5/091 (2013.01); A61B 5/4836 (2013.01); A61B 5/686 (2013.01); A61B 5/7264 (2013.01); A61B 5/7282 (2013.01); A61B 5/746 (2013.01); A61N 1/3627 (2013.01); A61N 1/36585 (2013.01); G16H 40/63 (2018.01); G16H 40/67 (2018.01); G16H 50/20 (2018.01); G16H 50/30 (2018.01); A61B 5/0816 (2013.01); A61B 7/04 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
1. A system for predicting a disease status of a patient, the system comprising:
a detector circuit configured to be coupled to an ambulatory medical device implanted in or associated with the patient, where the detector circuit is further configured to:
receive physiological information of the patient from a physiologic sensor of the ambulatory medical device;
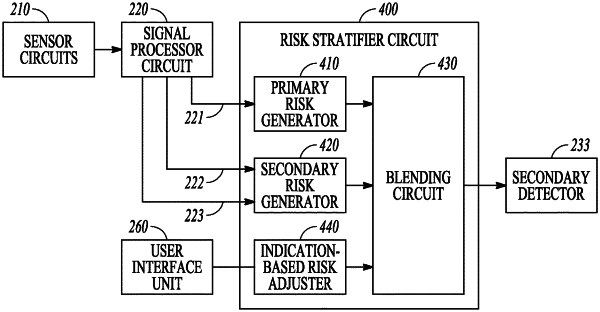
determine a risk indication associated with the disease status using the received physiological information;
generate a first detection indication using a first combination of signal metrics associated with the received physiological information and respective weight factors;
generate a second detection indication using a second combination of signal metrics associated with the received physiological information and respective weight factors,
the signal metrics in the second combination being more sensitive to the disease status than the signal metrics in the first combination,
wherein the first and second combinations of signal metrics and respective weight factors are different from each other and based at least in part on the determined risk indication;
and apply an information fusion model to the first detection indication, the second detection indication, and the risk indication to generate a composite prediction of the disease status;
and an output circuit configured to generate an alert about the composite prediction of the disease status to a user or a patient management process of the system;
where the alert includes a display of the composite prediction and one or more of: the first combination of signal metrics, the second combination of signal metrics, the first detection indication, and the second detection indication.
|