| CPC A61B 5/24 (2021.01) [A61B 5/1107 (2013.01); A61B 5/1122 (2013.01); A61B 5/1124 (2013.01); A61B 5/224 (2013.01); A61B 5/389 (2021.01); A61B 5/6824 (2013.01); A61F 2/54 (2013.01); A61F 2/583 (2013.01); A61F 2/72 (2013.01); A61H 1/0237 (2013.01); A61H 1/0274 (2013.01); A61B 5/1128 (2013.01); A61B 5/225 (2013.01); A61B 5/4052 (2013.01); A61B 5/4082 (2013.01); A61B 5/6825 (2013.01); A61B 5/6826 (2013.01); A61B 2505/09 (2013.01); A61F 2/70 (2013.01); A61F 2002/543 (2013.01); A61F 2002/6872 (2013.01); A61H 2201/501 (2013.01); A61H 2205/06 (2013.01); A61H 2205/065 (2013.01); A61H 2205/067 (2013.01); A61H 2205/10 (2013.01); A61H 2230/08 (2013.01); A61H 2230/085 (2013.01); A61H 2230/60 (2013.01)] | 16 Claims |
|
1. A method of treating a paretic limb of a patient, the method comprising:
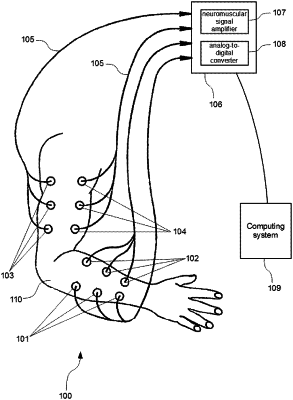
obtaining a neuromuscular-to-motion decoder using a computing system that includes a memory, a processor, and instructions stored in the memory executable by the processor, the instructions comprising functionality to execute a mapping method that maps first neuromuscular signals to first motion signals during a person performing a predefined exercise with a healthy limb, the mapping of the first neuromuscular signals to the first motion signals is performed using a method selected from the group consisting of a machine learning method, a statistical method, a data mining method and any combination of the machine learning method, statistical method and data mining method, the first neuromuscular signals having been generated by at least first and second neuromuscular sensors situated at first predefined locations on or in agonist and antagonist muscles of the healthy limb of the person during the person performing the predefined exercise, the first motion signals having been generated by a first plurality of motion sensors situated at second predefined locations on the healthy limb during the person performing the predefined exercise;
respectively placing at least third and fourth neuromuscular sensors at third predefined locations on or in the agonist and antagonist muscles of a paretic limb of the patient, the agonist and antagonist muscles of the paretic limb corresponding to the agonist and antagonist muscles of the healthy limb, the third predefined locations corresponding to the first predefined locations, the third and fourth neuromuscular sensors configured to produce second neuromuscular signals upon the patient attempting to perform the predefined exercise with the paretic limb;
inputting the second neuromuscular signals to the neuromuscular-to-motion decoder for causing the neuromuscular-to-motion decoder to output first motion commands;
placing a second plurality of motion sensors at fourth predefined locations on the paretic limb, the fourth predefined locations on the paretic limb corresponding to the second predefined locations of the healthy limb, the second plurality of motion sensors configured to produce second motion signals upon the patient attempting to perform the predefined exercise with the paretic limb;
producing trajectory data defining a trajectory to be followed by the paretic limb depending on a deviation between the second motion signals and predefined exercise data defining the predefined exercise;
producing second motion commands depending on the trajectory data to be followed by the paretic limb;
producing final motion commands depending on the first motion commands and the second motion commands; and
sending the final motion commands to a body actuator associated to the paretic limb to cause the body actuator to stimulate the paretic limb to perform the predefined exercise,
one or more of the first, second, third and fourth neuromuscular sensors being a sensor selected from the group consisting of an electromyography sensor, an electroneurography sensor, an ultrasound sensor, and an optical sensor,
one or more of the first and second plurality of motion sensors being selected from the group consisting of an inertial sensor, a magnetic sensor, and an optical sensor.
|