| CPC A61B 5/061 (2013.01) [A61B 5/0084 (2013.01); A61B 5/064 (2013.01); A61B 5/7425 (2013.01); A61B 8/12 (2013.01); G06T 7/33 (2017.01); A61B 5/0066 (2013.01); A61B 5/0073 (2013.01); A61B 5/0075 (2013.01); A61B 5/0086 (2013.01); A61B 5/066 (2013.01); A61B 2090/3966 (2016.02); G06T 2207/10016 (2013.01); G06T 2207/10072 (2013.01); G06T 2207/10121 (2013.01); G06T 2207/10132 (2013.01); G06T 2207/20101 (2013.01); G06T 2207/20221 (2013.01); G06T 2207/30101 (2013.01); G06T 2207/30172 (2013.01); G06T 2207/30204 (2013.01)] | 24 Claims |
|
1. An apparatus, comprising:
a processor configured for communication with one or more extraluminal imaging devices, wherein the processor is configured to:
receive, from the one or more extraluminal imaging devices, an angiographic image of a vessel while contrast agent is present in the vessel;
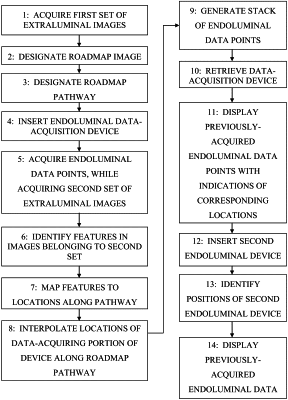
designate the angiographic image as a roadmap image;
generate a pathway in the roadmap image, wherein the pathway is representative of a shape of the vessel;
receive, from the one or more extraluminal imaging devices, a fluoroscopic image of the vessel;
identify three or more features in the fluoroscopic image, wherein the three or more features represent radiopaque portions of an endoluminal device positioned within the vessel;
determine an arrangement of the three or more features, wherein the arrangement of the three or more features is defined by a first vector corresponding to a first pair of the three or more features and a second vector corresponding to a different, second pair of the three or more features;
transform the fluoroscopic image based on a comparison of the pathway and the arrangement of the three or more features, wherein transformation includes mapping the three or more features to corresponding locations on the pathway such that the arrangement of the three or more features is fit to the shape of the vessel; and
output, to a display in communication with the processor, a mapped image based on the mapping.
|