| CPC A61B 5/0031 (2013.01) [A61B 5/1495 (2013.01); A61B 5/14532 (2013.01); A61B 5/7246 (2013.01); A61B 5/743 (2013.01); A61B 5/1118 (2013.01); A61B 5/14503 (2013.01); A61B 2560/0223 (2013.01); A61B 2560/0228 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
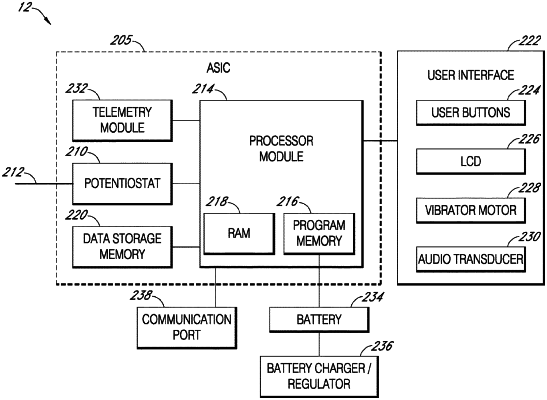
13. An analyte sensor system comprising:
an analyte concentration sensor;
a monitoring device, wherein the monitoring device is configured to detect when an analyte concentration value as measured by the analyte concentration sensor indwelling in a biological system; and
a processor, wherein the processor is a component of the monitoring device or of a device or a server operatively coupled to the monitoring device, wherein the processor is being programmed to perform operations comprising:
measuring analyte concentration values using an indwelling analyte concentration sensor to
obtain an indwelling analyte concentration sensor reading;
determining a first slow-moving average of the measured analyte concentration values of the analyte over a first period of time, and basing a first apparent sensitivity of the indwelling analyte concentration sensor based at least in part on the first slow-moving average;
following the first determining, determining a second slow-moving average of the measured analyte concentration values of the analyte over a second period of time, and basing a second apparent sensitivity of the indwelling analyte concentration sensor based at least in part on the second slow moving average; and
adjusting an actual sensitivity of the indwelling analyte concentration sensor to an adjusted value based on a difference between the first apparent sensitivity and the second apparent sensitivity when the difference between the first apparent sensitivity and the second apparent sensitivity meets a predetermined criteria, wherein the predetermined criteria is based on a range of acceptable sensitivity changes with respect to time.
|