| CPC H04N 23/611 (2023.01) [G06V 40/18 (2022.01); H04N 23/45 (2023.01); H04N 23/56 (2023.01); H04N 23/67 (2023.01); H04N 23/69 (2023.01); H04N 23/698 (2023.01)] | 3 Claims |
|
1. An iris image acquisition system for expanding an iris recognition range, the system comprising:
a wide-angle face recognition camera estimating a position of a face and eyes by photographing a subject;
a narrow-angle iris photographing camera provided with a zoom lens and a focus lens adjustment function to photograph a subject's iris image;
a near-infrared LED configured to emit near-infrared light to a photographing area of the iris photographing camera when the iris photographing camera is operated;
a distance sensor configured to measure a distance to the subject;
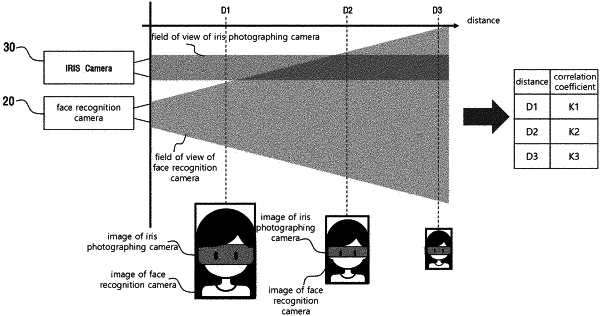
a mapping information database configured to record and store geometric mapping information generated on the basis of distance-specific correlation between the face recognition camera and the iris photographing camera; and
a controller configured to control operations of the face recognition camera, the iris photographing camera, the near-infrared LED, and the distance sensor, and control a direction, zoom, and focusing of the iris photographing camera according to information including subject eye position information acquired through the image acquired by the face recognition camera, distance information on the distance to the subject, the distance information being acquired through a sensor signal of the distance sensor, and the geometric mapping information of the mapping information database, the geometric mapping information being mapped to the distance information,
wherein the geometric mapping information of the mapping information database is generated on the basis of a correlation coefficient according to a distance between the subject and the face recognition camera and iris photographing camera, and
the correlation coefficient is calculated for each of a plurality of sections by generating first data on the basis of zoom information and focusing information by the distance to the subject, extracting a plurality of reference points whose rate of change according to the distance of the focusing information exceeds a predetermined first threshold point, and dividing the first data into the plurality of sections on the basis of the plurality of reference points.
|