| CPC G05B 19/406 (2013.01) [B23K 26/032 (2013.01); B23K 26/0876 (2013.01); B23K 26/38 (2013.01); B23K 26/703 (2015.10); B23K 37/006 (2013.01); B23K 37/0235 (2013.01); B23K 37/0408 (2013.01); B23K 2101/18 (2018.08); G05B 2219/45041 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
16. A method carried out by a computing system, the method comprising:
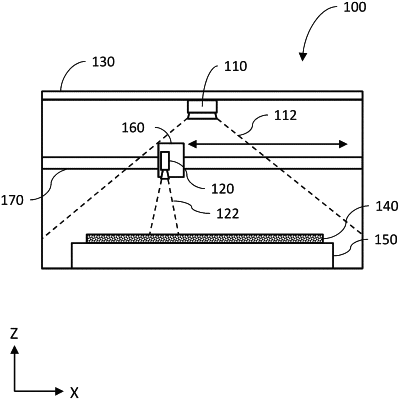
accessing an execution plan for a computer-numerically-controlled machine, the execution plan describing actions to be performed by at least one component of the computer-numerically-controlled machine in order to deliver electromagnetic energy for causing one or more changes in a material;
prior to execution of the execution plan by the computer-numerically-controlled machine, determining expected sensor data for at least one sensor of the computer-numerically-controlled machine based on the execution plan;
causing the computer-numerically-controlled machine to execute the execution plan and thereby deliver the electromagnetic energy for causing one or more changes in the material;
while the computer-numerically-controlled machine is executing the execution plan, obtaining actual sensor data generated by the at least one sensor of the computer-numerically-controlled machine and comparing the actual sensor data with the expected sensor data;
detecting an occurrence of an anomalous condition at the computer-numerically-controlled machine based on the comparison indicating at least a threshold deviation of the actual sensor data from the expected sensor data; and
based on detecting the occurrence of the anomalous condition, causing the computer-numerically-controlled machine to perform an action comprising at least one of: (i) reducing an output of the electromagnetic energy, (ii) blocking the electromagnetic energy, (iii) reducing a thermal output of one or more heat generating components of the computer-numerically-controlled machine, or (iv) locking a lid of the computer-numerically-controlled machine.
|