| CPC B29C 64/118 (2017.08) [D01F 8/12 (2013.01); D01F 8/14 (2013.01); B29K 2021/003 (2013.01); B29K 2077/00 (2013.01); B29K 2995/0046 (2013.01); B33Y 10/00 (2014.12); B33Y 70/10 (2020.01)] | 29 Claims |
|
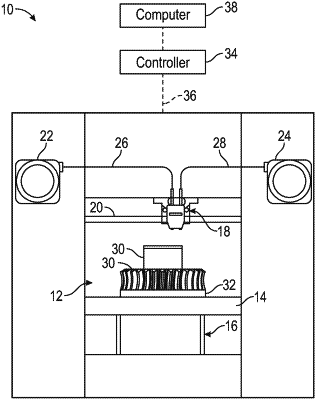
1. A filament for use in an extrusion-based additive manufacturing system, the filament comprising:
a core compositionally comprising an elastomeric core material having a flexural modulus of less than 31,000 psi and a durometer of less than 80 Shore A; and
a shell covering the core and having a thickness t, the shell compositionally comprising a non-elastomeric thermoplastic shell material that is substantially miscible with the elastomeric core material and has the same monomer chemistry as the elastomeric core material, and wherein the non-elastomeric thermoplastic shell material has a flexural modulus that is at least five times greater than the flexural modulus of the elastomeric core material,
wherein the shell provides sufficient stiffness to the filament such that filament can be utilized as a feedstock in the extrusion-based additive manufacturing system.
|