| CPC G01W 1/06 (2013.01) | 7 Claims |
|
1. An automatic recognition method for a dry quasi-stationary front in Kunming, Yunnan, China, comprising the following steps:
S1: physically measuring, with a sounding balloon, from an atmosphere an atmospheric temperature at 2 m above a point at ground surface and an atmospheric temperature at each layer of each point, where each point denotes a respective horizontal position and each layer denotes a respective height that is between the ground surface and a height corresponding to 650 hPa, and obtaining geopotential height data;
S2: calculating, by a differential method, a temperature lapse rate between each layer of each point between the ground surface and the height corresponding to 650 hPa, and acquiring a maximum inversion trend value of each point;
S3: acquiring an initially selected inversion distribution based on the maximum inversion trend value;
wherein step S3 comprises the following sub-steps:
S301: taking γt as a preset threshold in consideration of three types of inversion: weak lapse, strong inversion, and isothermal;
S302: acquiring the initially selected inversion distribution when the maximum inversion trend value is less than or equal to the preset threshold γt, wherein γt=0.1° C./100 m; and
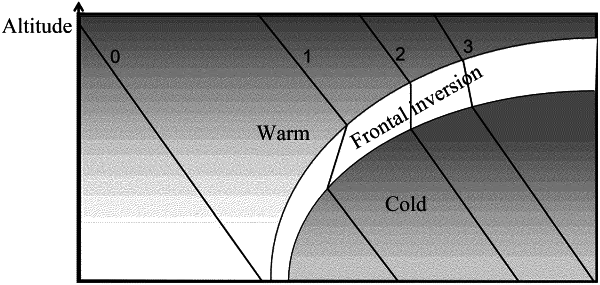
S303: determining that there is no quasi-stationary front in Kunming, Yunnan, China if there is no inversion at any point in an analysis area, and ending a recognition process;
S4: removing a nighttime clear sky radiation inversion from the initially selected inversion distribution, retaining only a frontal inversion, and binarizing (0, 1);
S5: finding a boundary between inversion and non-inversion on a binarized (0, 1) inversion distribution, and acquiring candidate frontal points;
S6: calculating an east-west distance between each of the candidate frontal points and an overall average position thereof, removing an abnormal candidate frontal point based on the east-west distance, and acquiring frontal nodes;
S7: removing meso- and micro-scale systems; and
S8: performing one-dimensional Gaussian filtering on longitude data of the frontal nodes based on a removal result, and connecting the filtered frontal nodes to acquire a quasi-stationary front in Kunming, Yunnan, China,
wherein in step S8, the one-dimensional Gaussian filtering is expressed as follows:
 wherein, G(x) denotes a curve acquired after the one-dimensional Gaussian filtering; σ denotes a smoothing parameter; σ=4 and x denotes a data sequence for filtering; and e denotes a natural constant.
|