| CPC H04W 28/0289 (2013.01) [H04W 40/02 (2013.01); H04W 40/34 (2013.01); H04W 88/04 (2013.01); H04W 88/06 (2013.01)] | 19 Claims |
|
1. A method of controlling communications within a wireless communications network comprising a plurality of infrastructure equipment each being configured to communicate with one or more others of the infrastructure equipment via a backhaul communications link, one or more of the infrastructure equipment each being configured to communicate with one or more communications devices via an access link, the method comprising:
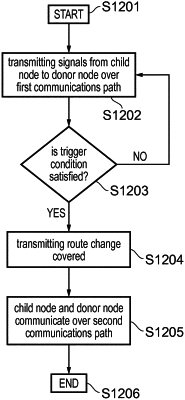
communicating, with a first of the infrastructure equipment acting as a donor node connected to a core network part of the wireless communications network, signals representing data by a second of the infrastructure equipment over a first communications path via one or more others of the infrastructure equipment acting as relay nodes, the second infrastructure equipment being a child node and one of the one or more other infrastructure equipment acting as the relay nodes or the donor node being a parent node, the parent node being connected to the child node via a backhaul communications link and configured to allocate uplink communications resources to the child node,
determining, by a triggering infrastructure equipment which is one of the child node and the parent node, that a trigger condition for the child node to communicate with the donor node over a second communications path via one or more other of the infrastructure equipment acting as relay nodes is satisfied, the second communications path being different to the first communications path,
transmitting a route change command to the other of the child node and the parent node, to the triggering infrastructure equipment or when the child node is the triggering infrastructure equipment, transmitting the route change command to one of the infrastructure equipment acting as relay nodes on the second communications path, the route change command indicating that the child node should communicate with the donor node over the second communications path, and
communicating, by the child node, with the donor node over the second communications path,
wherein the determining that the trigger condition is satisfied comprises at least a determination that at least one quality of service requirement cannot be guaranteed by the parent node.
|