| CPC H04W 24/04 (2013.01) [H04W 40/34 (2013.01); H04W 76/19 (2018.02); H04L 45/02 (2013.01)] | 20 Claims |
|
1. A child integrated access backhaul (IAB) node configured to communicate with a first parent IAB node and a descendant IAB node over a backhaul network, the child IAB node comprising:
processing circuitry configured to:
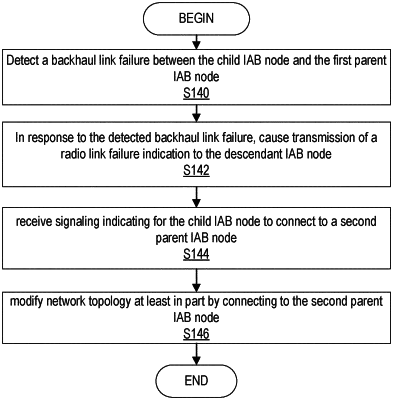
detect a backhaul link failure between the child IAB node and the first parent IAB node;
in response to the detected backhaul link failure, cause transmission of a radio link failure indication to the descendant IAB node, the radio link failure indication being configured to cause each descendant IAB node in an established communication path receiving the radio link failure indication to modify data transmission and remain on the established communication path to the child IAB node;
receive signaling indicating for the child IAB node to connect to a second parent IAB node; and
modify network topology at least in part by connecting to the second parent IAB node.
|