| CPC H04B 7/0634 (2013.01) [H04B 7/0626 (2013.01); H04B 7/0639 (2013.01); H04B 7/0691 (2013.01)] | 15 Claims |
|
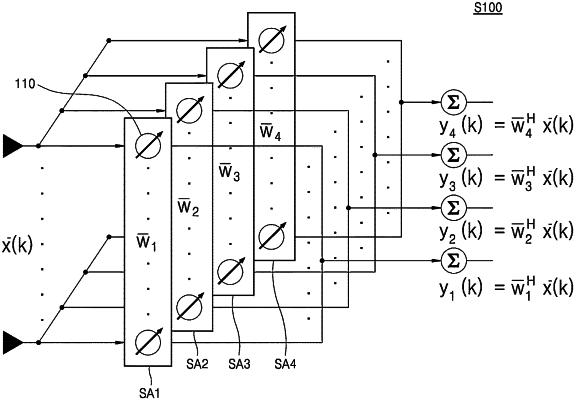
1. A beam search method using an active phased array antenna, wherein the beam search method uses a single tile-type phased array antenna including a plurality of radiating elements arranged in a matrix form, and the phased array antenna comprises a plurality of sub-arrays including the plurality of radiating elements and arranged in one direction, comprises:
calculating a beam coefficient application vector for each of the sub-arrays by using a received signal for each of the sub-arrays and a beam coefficient for each of the sub-arrays;
determining, as an initial value, a beam coefficient of an effective sub-array corresponding to a maximum value from among absolute values of beam coefficient application vectors for each of the sub-arrays; and
performing a monopulse algorithm based on the initial value, to obtain an expanded beamwidth greater than a reference beamwidth, which is a range of a beam detected by the phased array antenna,
wherein the monopulse algorithm is performed on an effective sub-array corresponding to the initial value, and the performing of the monopulse algorithm to obtain the expanded beamwidth further comprises:
determining a midpoint of the effective sub-array; and
calculating a summation coefficient for radiating elements arranged on both sides of the midpoint,
wherein the summation coefficient comprises: a first summation coefficient for a first radiating element group arranged on one side of the midpoint; and a second summation coefficient for a second radiating element group arranged on the other side of the midpoint, and
the effective sub-array comprises an overlapping portion including overlapping elements used for both calculation of the first summation coefficient and calculation of the second summation coefficient.
|