| CPC G16H 50/30 (2018.01) [G06F 17/11 (2013.01); G06F 30/20 (2020.01); G16H 40/20 (2018.01); G16H 50/50 (2018.01); G16H 50/70 (2018.01); G16Z 99/00 (2019.02); G01W 1/02 (2013.01); G06F 2111/10 (2020.01); Y02A 90/10 (2018.01)] | 19 Claims |
|
1. A method of decreasing hospital and clinic admission and readmission rates of a subject residing in a climate region and predisposed to experiencing weather-associated new onset migraine headache (NOH), the method comprising:
(I) generating a model set of equations for predicting a risk of subjects who suffer from weather-associated medical conditions of being admitted to the hospital, wherein the weather-associated medical condition is NOH, wherein generating comprises the steps of:
(a) identifying the climate region in which the hospital is located;
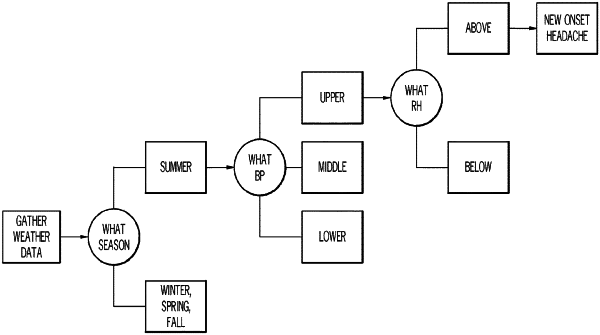
(b) collecting daily mean barometric pressure (BP) data for the year and dividing the mean BP data into upper, lower and middle quantiles;
(c) collecting daily hospital admissions data for a subject cohort for the year, said subject cohort consisting of subjects known to suffer from a weather-associated medical condition and who have been admitted to a hospital at least once previously due to experiencing an adverse event associated with the condition, to calculate a daily admission rate (AR) for each day of the year and to determine an upper quantile of days associated with the AR;
(d) determining a number of relevant seasons based on regression analysis of the upper BP quantile days and the upper AR quantile days;
(e) collecting weather parameter data across the year;
(f) applying linear regression analysis to generate a rank for each weather variable as a continuous predictor of the upper quantile AR (UQ-AR) days for each relevant season, for each BP quantile;
(g) identifying a best predictive single variable equation based on p-value and quasi-likelihood independence criterion (QIC) fit of the first-ranked weather variable in each relevant season, for each BP quantile;
(h) adding the next-ranked weather variable to the identified equation from (g) in each season, for each BP and determining if fit improves;
(i) repeating step (h) until addition of the next-ranked weather variable fails to improve fit, wherein the model comprises a set of equations for predicting a risk of subjects who suffer from weather-associated medical conditions of being admitted to the hospital at the completion of step (i);
(II) employing the model to determine which days are likely to be upper quantile admission rate days;
(III) allocating staff to work in the hospital on the days determined to be upper quantile admission rate days on the basis of the determination in step (II); and
(IV) administering a migraine headache preventative medical treatment to the subject on the days determined to be upper quantile admission rate days on the basis of the determination in step (II), wherein the migraine headache preventative medical treatment is selected from the group consisting of a beta blocker, a calcium channel blocker, an angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor, a tricyclic antidepressant, a serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI), an anti-seizure drug, a pain reliever, and combinations thereof.
|