| CPC G07C 13/00 (2013.01) [G06Q 2230/00 (2013.01); H04L 9/3239 (2013.01); H04L 9/3247 (2013.01); H04L 9/50 (2022.05); H04L 63/0428 (2013.01); H04L 63/08 (2013.01); H04L 2209/463 (2013.01)] | 12 Claims |
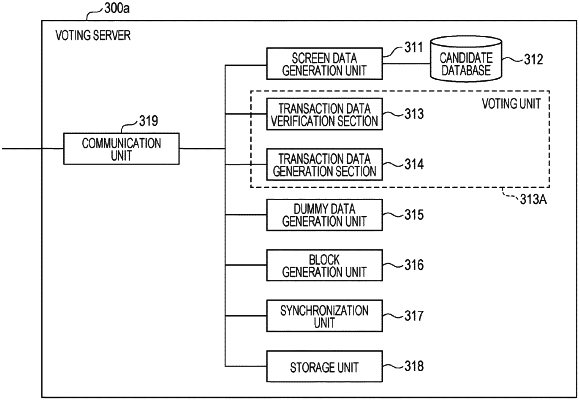
|
1. A method for controlling one of a plurality of voting servers in an electronic voting system, the method comprising:
receiving, over a network by the one of the plurality of voting servers and from a terminal, transaction data including voting data, wherein each of the plurality of voting servers includes a memory and a processor;
sharing, by the one of the plurality of voting servers with others of the plurality of voting servers, a number of dummy voting coins that is to be generated before an end of a voting period;
generating, at arbitrary timing in the plurality of voting servers and before the end of the voting period, dummy voting data including a plurality of dummy votes corresponding to the number of dummy voting coins, each of the plurality of dummy votes indicating a dummy vote for a random candidate among a plurality of candidates;
randomly arranging the transaction data including the voting data, and dummy transaction data including the dummy voting data that is not associated with the voting data in a sequence for abstracting identities of voters corresponding to the voting data;
generating, by the processor of the one of the plurality of voting servers, a block that includes the sequence of the randomly arranged the transaction data including the voting data, and the dummy transaction data including the dummy voting data;
connecting, by the processor of the one of the plurality of voting servers, the generated block to a blockchain, the blockchain being decentrally stored in the plurality of voting servers; and
synchronizing, by the processor of one of the plurality of voting servers, the blockchain with one other voting server among the plurality of voting servers.
|