| CPC G06T 7/74 (2017.01) [B64C 39/024 (2013.01); G06T 17/005 (2013.01); G06T 2207/10024 (2013.01); G06T 2207/10028 (2013.01); G06T 2207/10032 (2013.01); G06T 2207/20021 (2013.01); G06T 2207/30244 (2013.01)] | 10 Claims |
|
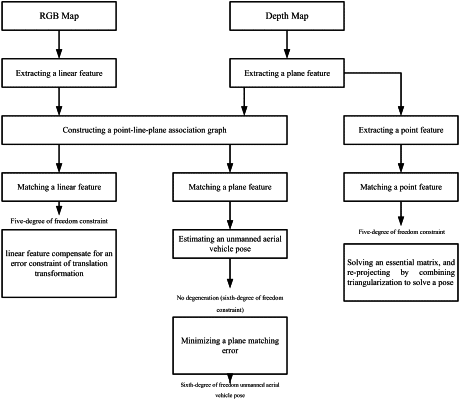
1. A pose estimation method for an unmanned aerial vehicle based on point, line and plane feature fusion, characterized by comprising:
S1 extracting an RGB image and a depth map by using an RGB-D camera;
S2 constructing a plane parameter space (PPS) according to the depth map, and mapping the depth map from a Cartesian space to the plane parameter space (PPS);
S3 constructing an inverse octree structure, comprising: reversely constructing cell nodes for the plane parameter space (PPS) according to octree data structure rules, and for each cell node, performing fitting by using Gaussian distribution;
S4 extracting one or more plane features, comprising: extracting the plane features on the basis of a feature extraction algorithm of the inverse octree;
S5 extracting a linear feature, comprising: extracting a linear feature on the RGB image by using a LSD algorithm detection;
S6 extracting a point feature by combining an RGB map;
S7 constructing a point-line-plane association graph;
S8 performing matching on the basis of the point-line-plane association graph of two adjacent frames; and
S9 estimating an unmanned aerial vehicle pose, comprising estimating the pose according to one or more matched plane features; and when the number of the one or more plane features is insufficient such that the pose can't be solved, then estimating the pose by combining the linear feature or by using a feature point feature.
|