| CPC G01S 7/4911 (2013.01) [G01S 7/4815 (2013.01); G02B 6/12007 (2013.01); G02B 6/29395 (2013.01)] | 10 Claims |
|
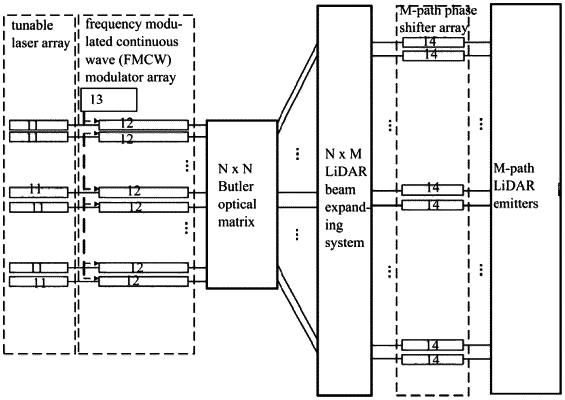
1. An integrated two-dimensional multi-beam LiDAR transmitter based on a Butler matrix, comprising
a tunable laser array,
a frequency modulated continuous wave modulator array,
an N×N Butler optical matrix network,
an N×M optical beam expanding network,
an M-path phase shifter array, and
an M-path two-dimensional LiDAR emitters,
wherein the tunable laser array is a narrow linewidth laser array, and N-path narrow linewidth continuous light output by the tunable laser array passes through the frequency modulated continuous wave modulator array to generate N-path frequency modulated continuous wave signals;
after being processed by the N×N Butler matrix network and the N×M optical beam expanding network, the energy of each path of the frequency modulated continuous optical signal is evenly distributed to M-path output ports, and output signals of adjacent output ports have equal phase differences;
the M-path phase shifter array generates equal-difference phases with continuously tunable phase differences for the M-path optical signals output by the M-path output ports;
the M-path optical signals with continuously adjustable phase differences are transmitted by the M-path two-dimensional LiDAR emitters so that no more than N different two-dimensional steerable optical beams are realized, wherein N=2n (n=1, 2, . . . ), M=2K×N (K=1, 2, . . . ).
|