| CPC G01R 33/3415 (2013.01) [A61B 5/055 (2013.01); G01R 33/385 (2013.01)] | 5 Claims |
|
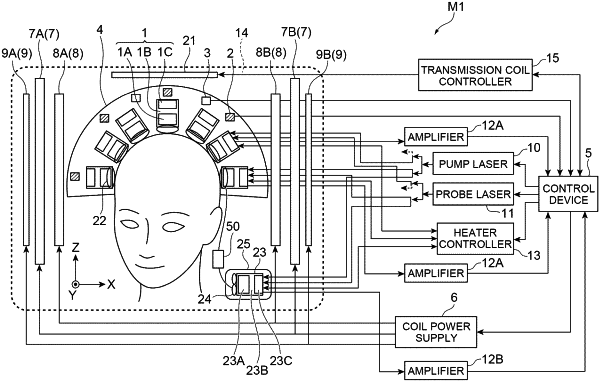
1. A brain measurement system comprising:
a static magnetic field coil for applying a static magnetic field;
a gradient magnetic field coil for applying a gradient magnetic field;
a transmission coil for transmitting a transmission pulse having a predetermined frequency;
a plurality of receiving coils for detecting a nuclear magnetic resonance signal generated by transmission of the transmission pulse and converting the nuclear magnetic resonance signal into a current;
a plurality of resonance adjustment circuits provided corresponding to each of the plurality of receiving coils for outputting a signal having a predetermined resonance frequency of a current output from the receiving coil;
a plurality of detection units provided corresponding to each of the plurality of resonance adjustment circuits for detecting the signal having the resonance frequency output from the resonance adjustment circuit; and
a control device configured to control currents to be supplied to the static magnetic field coil and the gradient magnetic field coil to control the static magnetic field and a tilted magnetic field and control a current to be supplied to the transmission coil so that the transmission pulse is transmitted to a head portion of a subject to generate an MR image based on the signal detected by the detection unit,
wherein, when a direction parallel to a central axis of the head portion of the subject is defined as a Z-axis direction, the resonance frequency related to each of the plurality of resonance adjustment circuits is set according to a magnetic field gradient in the Z-axis direction generated by control of a position of the corresponding receiving coil in the Z-axis direction and the tilted magnetic field.
|